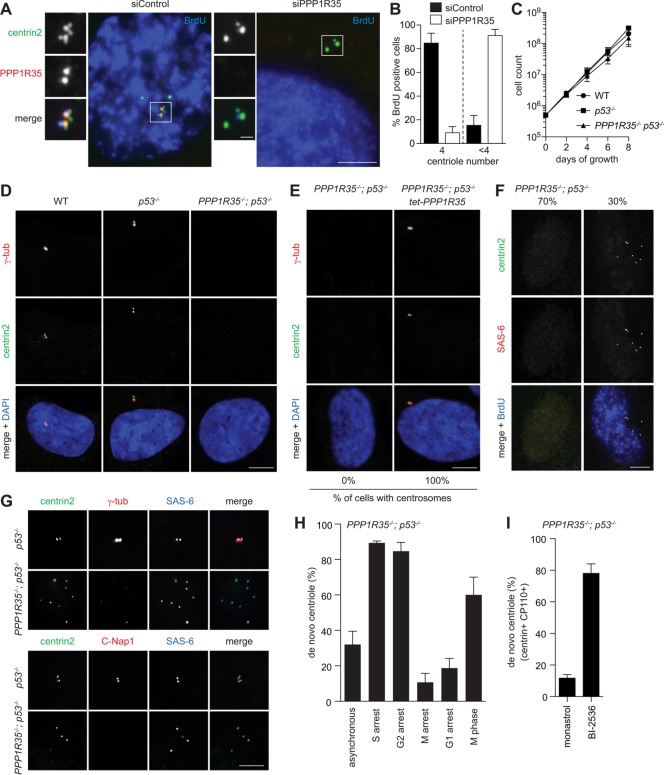
FIGURE 2:
Loss of PPP1R35 causes centriole destabilization during M-G1 transition. (A) PPP1R35 knockdown resulted in centriole number reduction. IF images of RPE1 cells in S phase (BrdU-positive) after PPP1R35 RNAi. Scale bar = 5 μm; 1 μm in inset. (B) Graph showing quantification of phenotypes in A. Data are means ± SD. N > 100, N = 3. (C, D) PPP1R35−/−; p53−/− cells continue to proliferate in the absence of centrosomes. Growth curves (C) and IF images (D) of PPP1R35−/−; p53−/− cells in comparison to wild-type and p53−/− cells. Data are means ± SD. n > 50, N = 3. Scale bar = 5 μm. (E) Centrosome defects in PPP1R35−/−; p53−/− cells are rescued by PPP1R35 expression. PPP1R35−/−; p53−/− cells infected with virus carrying tetracycline-inducible PPP1R35 were examined for the presence of centrosomes. Numbers in the merged image indicate the percentage of cells carrying centrosomes. Scale bar = 5 μm. (F, G) De novo centrioles, all of which carry the cartwheel but not the PCM, are detected in ∼30% of PPP1R35−/−; p53−/− cycling cells. PPP1R35−/−; p53−/− or control (p53−/−) cells growing asynchronously were examined with indicated antibodies. Note that weak centriolar but not strong PCM-associated γ-tubulin is present in de novo centrioles. Scale bar = 5 μm. (H) Centrioles in PPP1R35−/−; p53−/− cells are assembled de novo during S phase, but are disintegrated during M and G1. Graph showing percentage of PPP1R35−/−; p53−/− cells with de novo centrioles at different cell cycle stages. G1-arrest cells were generated by serum starvation for 48 h. S-, G2-, or M-arrest cells were generated by treating cells with aphidicolin, RO-3306, or Eg5 inhibitor for 20 h, respectively. In comparison with M-arrest, normal (nonarrested) M-phase cells in unsynchronized populations were also examined. Data are means ± SD. n > 100, N = 3. (I) PPP1R35−/−; p53−/− cells were allowed to enter mitosis in the presence of the Plk1 inhibitor (BI-2536), or Eg5 inhibitor (monastrol) as a control, and release to and arrest at G1 by Cdk inhibition with roscovitine for 16 h before fixation for examining de novo centrioles. Cells going through this type of manipulation are known to display donut-shaped, multilobed, or multiple small nuclei as described before (Tsou et al., 2009), and were thereby identified for analyses. In Plk1-inhibited cells arrested in G1, de novo centrioles that retained the cartwheel (SAS-6), centrin and CP110 were stably present. Quantifications are shown. Data are means ± SD. n > 100, N = 3.