Figure 1.
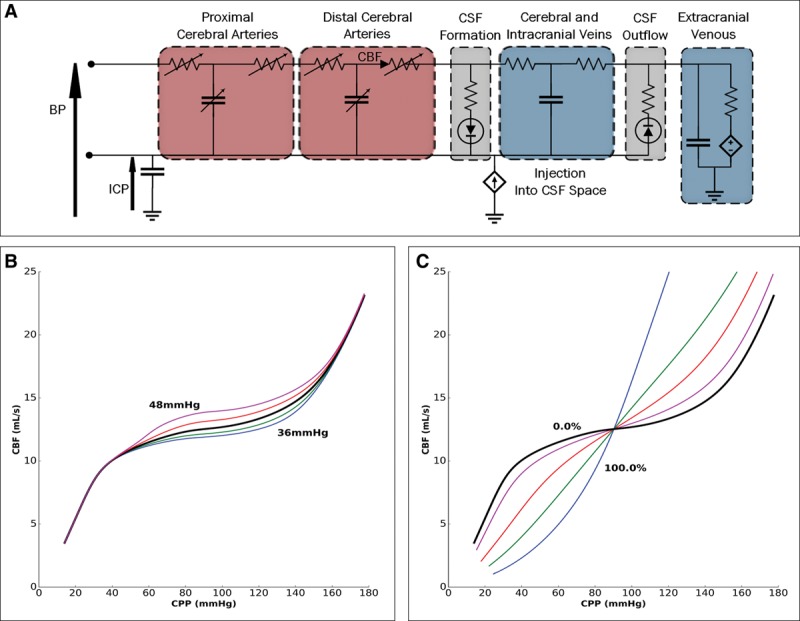
The electrical circuit equivalent of the lumped compartment model and some baseline physiologic operating characteristics. A, The model includes different segments: proximal and distal cerebral arteries, cerebral and intracranial veins, extracranial venous, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) formation and outflow. B, The dependence of cerebral blood flow (CBF) on cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) under steady-state conditions at various Paco2 values (36, 38, 40, 42, and 44 mm Hg). Increasing Paco2 increases CBF at any given CPP. C, The dependence of CBF on CPP when cerebral autoregulation (CA) gain varies. CPP variation leads to more alteration in CBF as CA impairment increases (0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100%). BP = blood pressure, ICP = intracranial pressure.
