Figure 1.
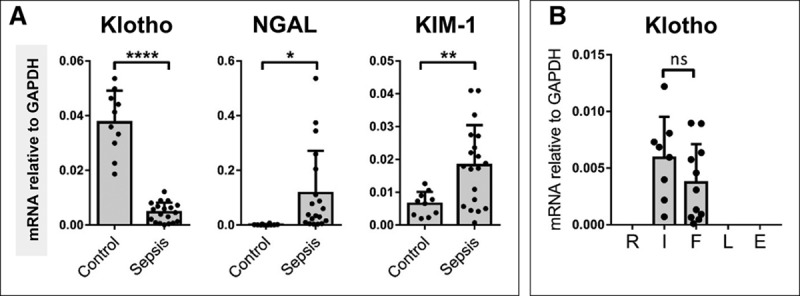
Renal Klotho levels are reduced in critically ill patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) while renal damage markers are increased. A, Postmortem kidney biopsies were collected from patients with sepsis-AKI (n = 19). Kidney tissue was also obtained from control subjects (n = 10). Klotho, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), and kidney injury molecule (KIM)-1 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression were determined by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction using glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as a housekeeping gene. B, Sepsis-AKI patients (n = 19) were also categorized by the extent of renal failure, Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss of kidney function and End-stage kidney disease (RIFLE) criteria. Each dot represents an individual subject, and the bars represent the mean ± sd. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ****p < 0.0001. ns = not significant.
