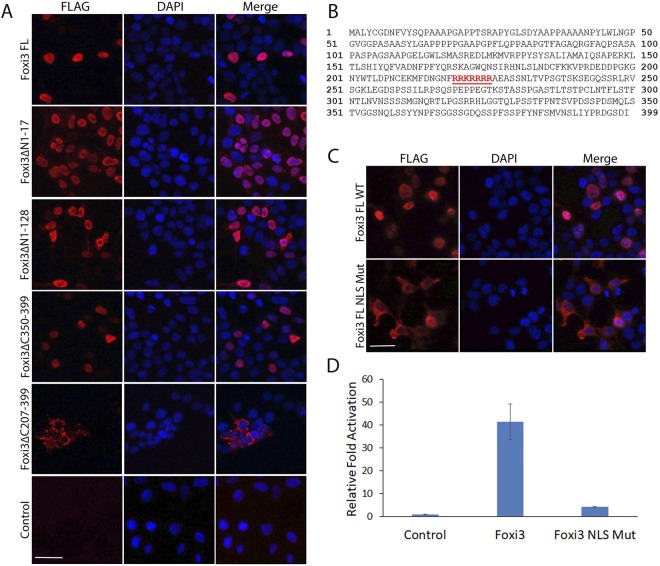
Figure 2.
Characterization of nuclear localization sequence (NLS) in Foxi3. (A) Immunostaining using FLAG antibody in HEK-293T cells transfected with FLAG-tagged N-terminal and C-terminal truncations of Foxi3 described in Fig. 1. DAPI was used as nuclear stain. Deletion of the region from AA207–399 (Foxi3ΔC207–399) prevents nuclear localization. (B) A nuclear localization sequence (219–225aa, shown in red) was predicted for Foxi3 protein using the NucPred tool (C) The predicted NLS was mutated in Foxi3 (Foxi3 FL NLS Mut) and transfected in HEK-293T cells. Wild-type Foxi3 (Foxi3 FL WT) was used as control. Mutation of the predicted NLS abolishes nuclear localization. (D) Mutation of the predicted NLS abolishes Foxi3 activity. AE4 promoter activity was measured after co-transfection of AE4 luciferase reporter with wild-type Foxi3 (Foxi3) or Foxi3 with mutated NLS (Foxi3 NLS Mut). HEK-293T cells were transfected with 250 ng of AE4 luciferase reporter along with 250 ng of either with wild-type Foxi3 (Foxi3) or Foxi3 with mutated NLS (Foxi3 NLS Mut) coding constructs as indicated. AE4 promoter linked Luciferase activity is shown as relative fold activation compared with control. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and was repeated at least three times. Error bars represent standard deviations calculated from the biological triplicates. Δ: deletion, FL: full-length, NLS: nuclear localization sequence. Scale bars: 50 µm.