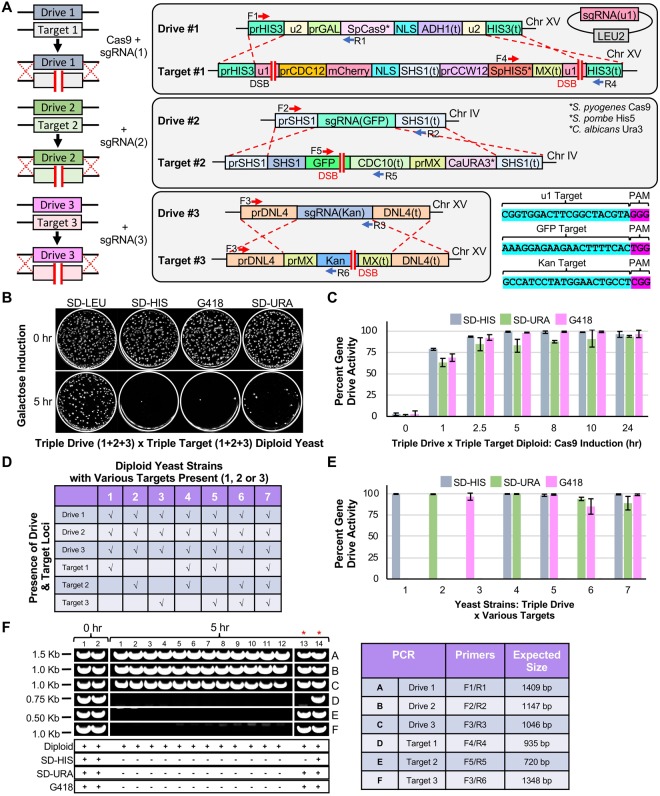
Figure 2.
Design of a CRISPR/Cas9-based gene drive system in S. cerevisiae across three loci. (A) Left, An artificial gene drive was installed at three loci in haploid yeast. Each drive system (Drive 1–3) contained a guide RNA cassette targeting an artificial target (Target 1–3) at the same locus. Only Drive 1 contained the cassette for S. pyogenes Cas9. Right, Artificial (u1) and (u2) sites63 were used flanking the gene drive at the HIS3 locus (Chromosome XV) and the S.p.HIS5 selectable marker. The SHS1 locus (Chromosome IV) included a C-terminal GFP and C.a.URA3. DNL4 (Chromosome XV) was deleted with the KanR cassette. All sgRNAs were targeted to non-native sequences. The sgRNA(u1) cassette was on a high-copy plasmid (LEU2 marker). S.p.Cas9 was under control of the inducible GAL1/10 promoter. (B) Haploid yeast harboring the triple drive (GFY-3675) were mated to the triple target strain (GFY-3596) to form diploids. Cas9 expression was induced by galactose (0 or 5 hr). Cultures were diluted to 100–500 cells per plate, grown for 2 days, and transferred to SD-LEU, SD-HIS, SD-URA, and G418 plates. (C) A time course of galactose activation using the [GFY-3675 x GFY-3596] diploid in triplicate. Error, SD. (D) Seven haploid strains (GFY-3206, 3593, 3264b, 3578, 3594, 3623, and 3596) were tested as in (B) against the triple drive strain (GFY-3675). (E) Each of the diploids from (D) were cultured for 5 hr and quantified for drive success. Error, SD. (F) Clonal isolates were obtained from diploids generated in (B) at either 0 hr (2 isolates) or 5 hr activation of Cas9 (14 isolates). All yeast were confirmed as diploids and assayed on each media type (below). Diagnostic PCRs were performed on genomic DNA to detect the presence (or absence) of each locus; oligonucleotide (Supplementary Table 5) positions can be found in (A) and the expected sizes are illustrated (right). Two isolates (13,14) were chosen for their incomplete growth profile (red asterisks). Images were cropped from separate portions of larger gels or from independent DNA gels and are separated by white lines. The unedited images can be found in Supplementary Fig. S8.