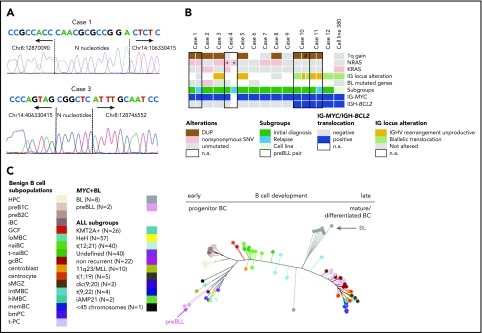
Figure 1.
Genetic and epigenetic characterization of the preBLL samples. (A) Verification of IG-MYC breakpoint junctions retrieved from exome sequencing data by Sanger sequencing in cases 1 and 3. Both breakpoints showed features of aberrant VDJ rearrangement, including localization within the VDJ region and occurrence of N nucleotides. Details provided in supplemental Figure 1. (B) Summary of recurrent copy number aberrations (CNAs) and single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) identified by whole-exome sequencing/whole-genome sequencing and OncoScan analysis. Of note is that only 1 preBLL case harbored a mutation (SMARCA4) in those genes recurrently mutated in BL (overview provided in supplemental Figure 2). (C) Phylogenetic tree based on the DNA methylation pattern of 1404 CpG loci described to be differentially methylated during B-cell development.26 In the analysis, 17 B-cell subpopulations from various differentiation states were included, which arranged themselves along the main trunk of the phylogenetic tree according to their differentiation stadia. The 2 preBLL cases clustered with the pB-ALL/LBL samples24,25,26 near the precursor B-cell subpopulations, whereas the BL samples were closer to the mature B-cell subpopulations. *Indicates that the NRAS mutation in case 4 differed between the ID and relapse samples. #Indicates that the 1q gain in sample 2 of case 10 occurred in comparison with sample 1 of case 10 in a subset of cells. DUP, duplication; n.a., not available.