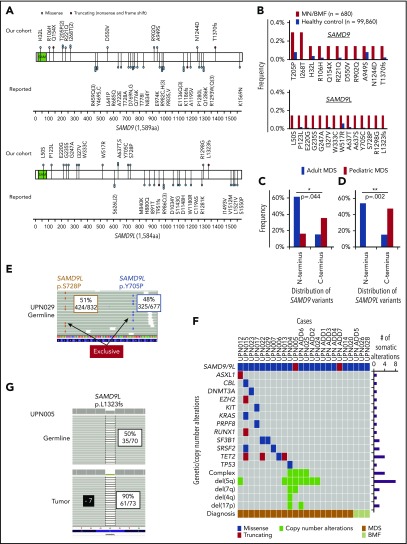
Figure 1.
Characteristic of GL SAMD9/SAMD9L variants in adult MDS. (A) Positions and types of GL SAMD9 and SAMD9L variants detected in adult patients with MDS and BMF (above the 2 genes). Reported SAMD9 and SAMD9L variants in familial pediatric MDS and BMFs are also depicted (below the 2 genes). Functional sterile α motif (SAM) is shown in green. (B) Frequencies of specific SAMD9 and SAMD9L GL variants in our cohort and ethnically matched healthy controls. Distribution of GL SAMD9 (C) and SAMD9L (D) variants between adult and pediatric MDS. Three genetic regions (N terminus, enter, and C terminus) were defined with equal number of base pairs and compared with each other. P values were calculated by Fisher’s exact test. (E) Biallelic GL variants of SAMD9L. Representative view of 2 independent GL SAMD9L variants (Tyr705Pro, Ser728Pro) in a patient (UPN029). Variant allele frequencies and counts of sequence reads in GL samples (CD3 positive lymphocyte) are shown in boxes. (F) Landscape of somatic mutations and CNAs in adult MDS patients with GL SAMD9/SAMD9L variants. Type of mutations, cytogenetics, and diagnosis, together with the number of somatic mutations/CNAs, are color coded as indicated. (G) A patient (UPN005) with a GL frameshift SAMD9L variant (Leu1323fs) and −7 simultaneously. Variant allele frequencies and counts of sequence reads in GL (CD3 positive lymphocyte) and tumor (bone marrow) are shown in boxes.