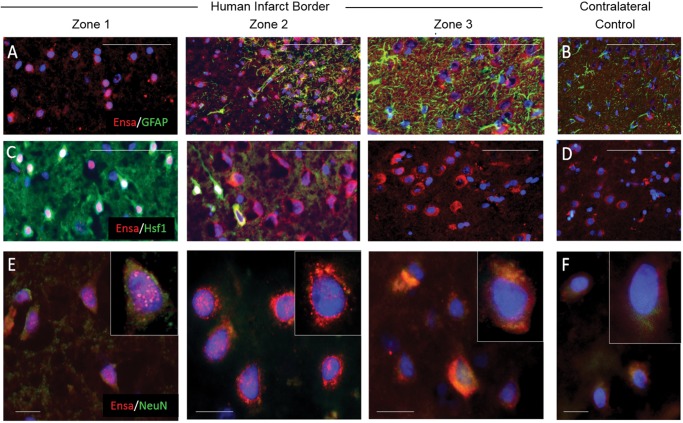
FIGURE 7.
Upregulation and nuclear translocation of αEnsa protein is detected in ischemic human neurons using a polyclonal rabbit-anti-αEnsa primary antibody. Immunofluorescent montage images of ischemic human cortex reveal αEnsa protein expression changes in distinct regions of infarcted brain (A, C), relative to controls (B, D). Double label immunofluorescent images demonstrate colocalization with NeuN in degenerating ischemic neurons, with punctate labeling and nuclear translocation seen in zones 1 and 2 (data are representatiave of findings in 5 postmortem cerebral infarcts); original magnification, 20× (A–D); 40× (E, F); scale bars, 50 µm (A–D) or 10 µm (E, F); αEnsa, red/CY3; GFAP, Hsf1, NeuN, green/FITC; nuclei, blue/DAPI.