FIGURE 8.
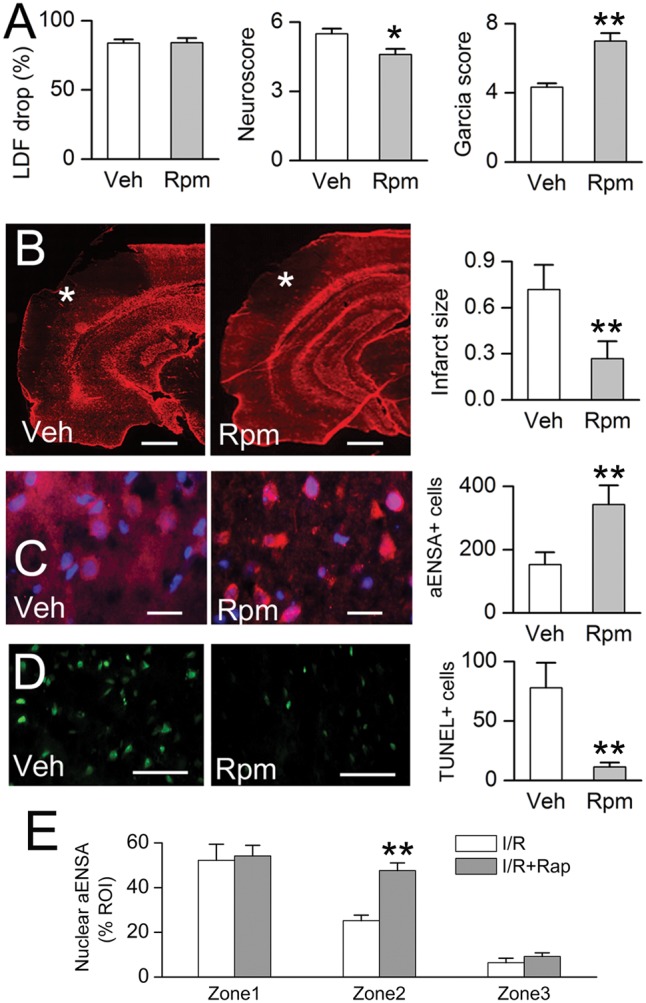
Rapamycin treatment is associated with reduced infarct size, increased nuclear αEnsa protein expression in Zone 2, and reduced cell death in rat MCAo. Laser Doppler flowmetry (LDF) at the time of MCAo, and Neuroscores and Garcia scores at 24 hours (A); GFAP labeling demonstrates reduction of infarct size in rapamycin-treated rats, relative to vehicle controls (data representative of 6 rats per group) (B). In Zone 2 of the ishemic cortex, immunolabeling in rapamycin treated rats demonstrates increased nuclear translocation of αEnsa (C), and decreased TUNEL labeling (D), relative to controls; scale bars, 500 µm (B); 10 µm (C); 100 µm (D); GFAP and αEnsa, red/CY3; terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL), green/FITC; nuclei, blue/DAPI. Rapamycin treatment increased nuclear translocation of αEnsa in Zone 2, but not Zones 1 or 3 (E). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
