Figure 3.
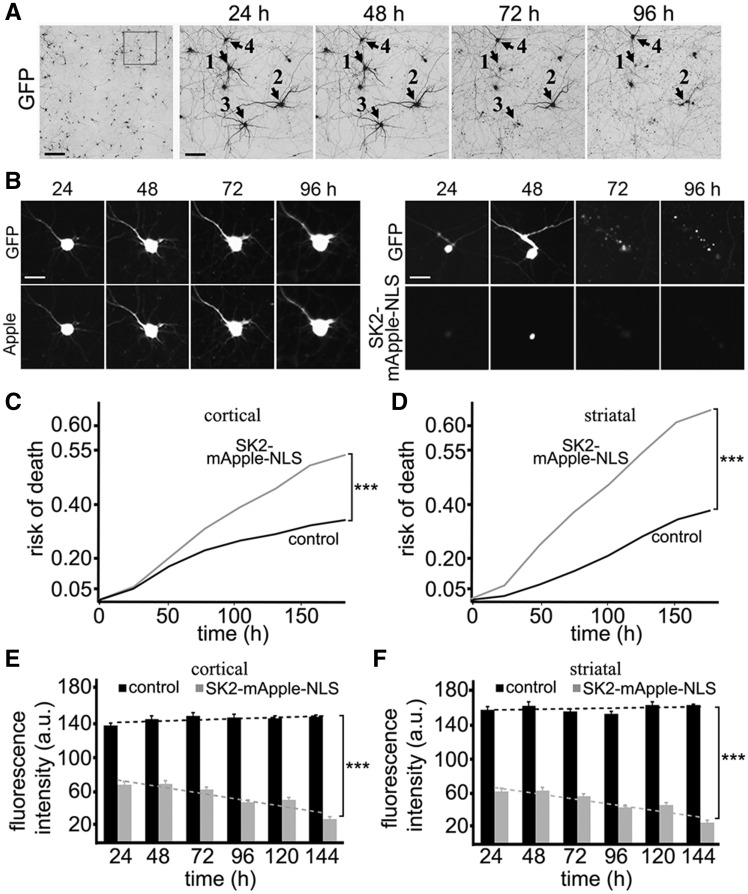
SK2 is neurotoxic to cortical and striatal neurons in a dose-dependent manner. (A) An example of survival analysis. Primary cortical neurons were transfected with GFP (a morphology and viability marker) and tracked with an automated microscope. Images collected after 24 h demonstrate the ability to return to the same field of neurons and to follow them over time. Each image is a montage of non-overlapping images captured in one well of a 24-well plate. Scale bar is 200 μm. A region from the original images at different time points is zoomed in to demonstrate longitudinal single-cell tracking (right panels). Black arrows depict three neurons that degenerate by 72 h (neurons 1 and 3) and by 96 h (neuron 2) after transfection. Neuron 4 survived the entire experiment. Scale bar is 50 μm. (B) Longitudinal imaging of a neuron expressing GFP and mApple (left panel) and a neuron expressing GFP and SK2-mApple-NLS (right panel). The left neuron remains alive throughout the experiment. The right neuron died by 72 h. Scale bar is 10 μm. (C) Primary cortical neurons were transfected either with GFP + mApple (control) or with GFP + SK2-mApple-NLS. Transfected neurons were tracked with an automated microscope. Cumulative risk of death was calculated from Kaplan–Meier curves (JMP software). Cumulative risk of death curves demonstrates that the SK2-mApple-NLS construct is neurotoxic. ***P < 0.001 (log-rank test). Two hundred neurons were analyzed. Results were pooled from three independent experiments. (D) Primary striatal neurons were transfected either with GFP + mApple (control) or with GFP + SK2-mApple-NLS. Transfected neurons were tracked with an automated microscope. Cumulative risk of death was calculated from Kaplan–Meier curves. Cumulative risk of death curves demonstrate that the SK2-mApple-NLS construct is also neurotoxic to striatal neurons. ***P < 0.001 (log-rank test). Two hundred neurons were analyzed. Results were pooled from three independent experiments. (E) The average mApple-fluorescence and SK2-mApple-NLS intensities and single neuron survival to determine the dose-dependent toxicity in cortical primary neurons that express the mApple or SK2-mApple-NLS construct. Neuronal survival is not affected by mApple expression. However, higher SK2-mApple-NLS intensity lead to higher risk of death. m(control) = 0.1487; m(SK2-mApple-NLS) = −0.4246. ***P < 0.0001 (t-test). One hundred fifty neurons were analyzed. Results were pooled from three independent experiments. (F) The average mApple-fluorescence and SK2-mApple-NLS fluorescence intensities and single neuron survival to determine the dose-dependent toxicity in striatal primary neurons that express the mApple or SK2-mApple-NLS construct. Note that neuronal survival is affected by SK2-mApple-NLS expression. m(control) = 0.1005; m(SK2-mApple-NLS) = -0.4476. ***P < 0.0001 (t-test). One hundred fifty neurons were analyzed. Results were pooled from three independent experiments.