Figure 5.
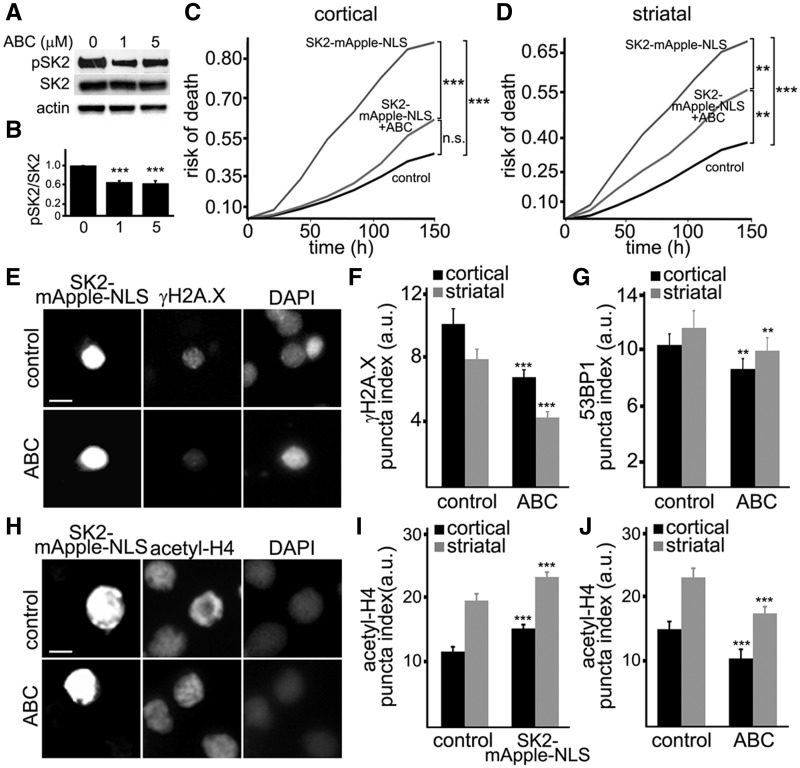
An inhibitor of SK2, ABC294640, mitigates neurotoxicity induced by ectopically expressed SK2. (A) Primary cortical neurons were treated with a vehicle or with different concentrations of ABC294640 (ABC, 1 and 5 µM). Neuronal lysates were then analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against phosphorylated SK2 (pSK2) and pan-SK2 (SK2). Actin was used as a loading control. (B) Quantification of pSK2 levels normalized to SK2 from (A). Results were pooled from three independent experiments. (C) Primary cortical neurons transfected with GFP and mApple (control) or with GFP and SK2-mApple-NLS constructs. Two cohorts of neurons that express SK2-mApple-NLS and GFP were treated with a vehicle (SK2-mApple-NLS) or 1 μM ABC294640 (SK2-mApple-NLS + ABC). Risk of death was calculated from Kaplan–Meier curves. The ABC294640 drug reduces the risk of death in SK2-mApple-NLS-expressing neurons. ***P < 0.001 (Log-Rank test). n.s., not significant (P = 0.06). (D) Primary striatal neurons transfected with GFP and mApple (control) or with GFP and SK2-mApple-NLS constructs. Neurons that express SK2-mApple-NLS and GFP were treated with a vehicle (SK2-mApple-NLS) or 1 μM ABC294640 (SK2-mApple-NLS + ABC). Risk of death was calculated from Kaplan–Meier curves. The ABC294640 drug reduces the risk of death in SK2-mApple-NLS-expressing striatal neurons. ***P < 0.001 (log-rank test), **P = 0.0058 (control vs SK2-mApple-NLS + ABC), and **P = 0.0061 (SK2-mApple-NLS vs SK2-mApple-NLS + ABC). One hundred fifty neurons were analyzed. Results were pooled from three independent experiments. (E) Cortical neurons were transfected with SK2-mApple-NLS, and treated with a vehicle (control) or 5 μM ABC294640 (ABC) for 24 h. Cells were fixed, stained with an antibody against γH2A.X and with the nuclear Hoechst dye (DAPI), and imaged. Note that SK2 inhibitor reduces the γH2A.X puncta index in SK2-mApple-NLS-expressing neurons compared to vehicle-treated transfected cells. Scale bar is 5 μm. (F) Quantification of the γH2A.X puncta index in cortical and striatal neurons transfected with SK2-mApple-NLS and treated with a vehicle (control) or 5 μM ABC294640 (ABC) for 24 h. ***P < 0.0001 (t-test). A.u., Arbitrary units. Three hundred neurons were analyzed from three independent experiments. (G) Quantification of the 53BP1 puncta index in cortical and striatal neurons transfected with SK2-mApple-NLS, treated with a vehicle (control) or 5 μM ABC294640 (ABC) for 24 h. **P = 0.0013 and **P = 0.0027 (t-test) for cortical and striatal neurons, respectively. A.u., Arbitrary units. Two hundred neurons were analyzed from three independent experiments. (H) Cortical neurons were transfected with SK2-mApple-NLS, and treated with a vehicle (control) or 5 μM ABC294640 (ABC) for 24 h. Cells were fixed, stained with an antibody against histone H4 (acetyl K5 + K8 + K12 + K16, acetyl-H4) and with the nuclear Hoechst dye (DAPI), and imaged. Scale bar is 5 μm. (I) Quantification of the acetyl-H4 puncta index in cortical and striatal neurons transfected with mApple (control) or with SK2-mApple-NLS construct. ***P = 0.0002 and ***P < 0.0001 (t-test) for cortical and striatal neurons, respectively. A.u., Arbitrary units. Two hundred neurons were analyzed from three independent experiments. (J) Quantification of the acetyl-H4 puncta index in cortical and striatal neurons transfected with SK2-mApple-NLS and treated with a vehicle (control) or with 5 μM ABC294640 (ABC). ***P = 0.003 and ***P = 0.0038 (t-test) for cortical and striatal neurons, respectively. A.u., Arbitrary units. Two hundred neurons were analyzed from three independent experiments.