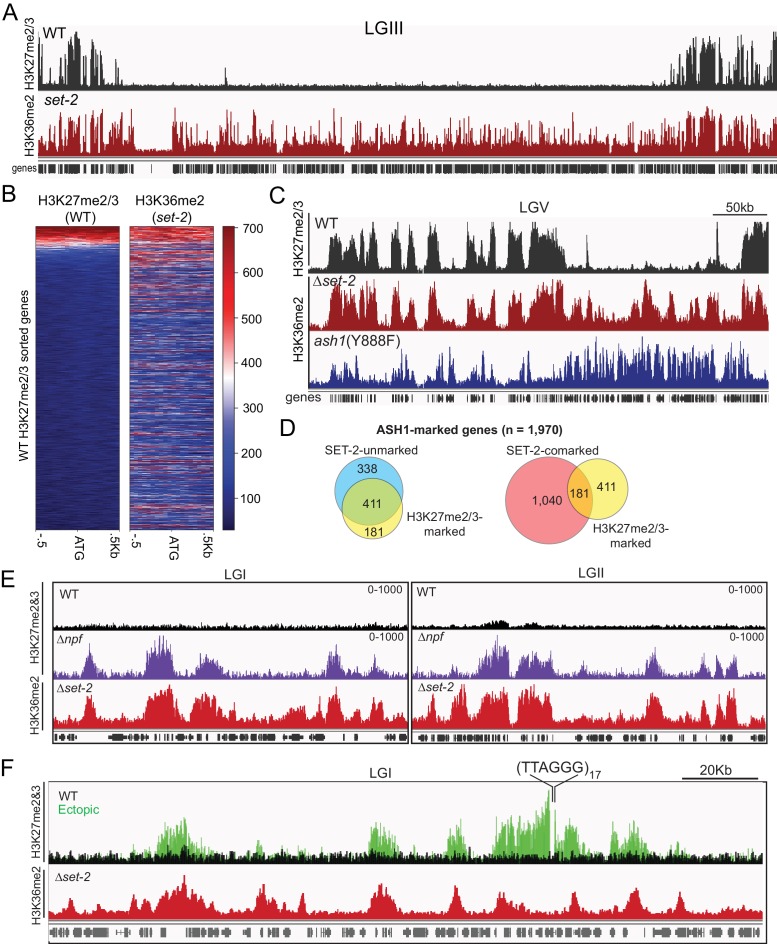
Figure 4. ASH1-catalyzed H3K36me2 delineates H3K27me2/3-competent chromatin.
(A) Representative IGV tracks for H3K27me2/3 in WT and H3K36me2 as catalyzed by ASH1. All of LGIII is shown. (B) Heatmap showing the distribution of average H3K27me2/3 signal intensity in WT (left) and ASH1-catalyzed H3K36me2 (right) across the promoter region of all genes. Genes are sorted by WT H3K27me2/3 intensity. (C) Representative IGV tracks of H3K27me2/3 in WT and H3K36me2 as catalyzed by ASH1 or SET-2. (D) Fraction of ASH1-marked genes co-marked by SET-2, SET-7, or both SET-2 and SET-7. The distribution of SET-7/ASH1-comarked genes (yellow circle) in the SET-2-comarked (red) and SET-2-unmarked (blue) compartments shows that most (411/592) ASH1/SET-7 doubly marked genes are not marked by SET-2. Statistical significance (two-tailed p-value<10−4) was determined by the Chi-square test. (E) H3K27me2/3 ChIPseq tracks from WT (black) andΔnpf (purple) strains are compared to H3K36me2 ChIPseq in Δset-2. Depicted regions were selected for their multiple aberrant domains of H3K27me3. (F) H3K27me2/3 ChIPseq track from WT (black) and ectopic telomere-repeat (green) strains are superimposed and compared to H3K36me2 ChIPseq in a Δset-2 strain.