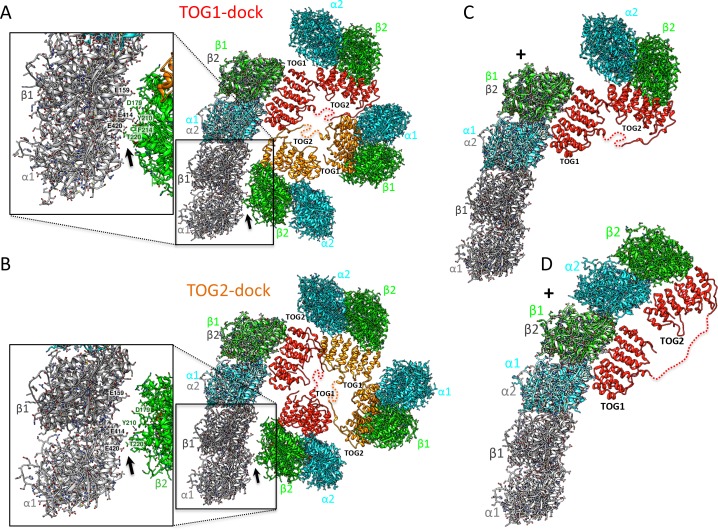
Figure 7. Docking of atomic structures onto protofilament ends reveals the molecular details of unfurling.
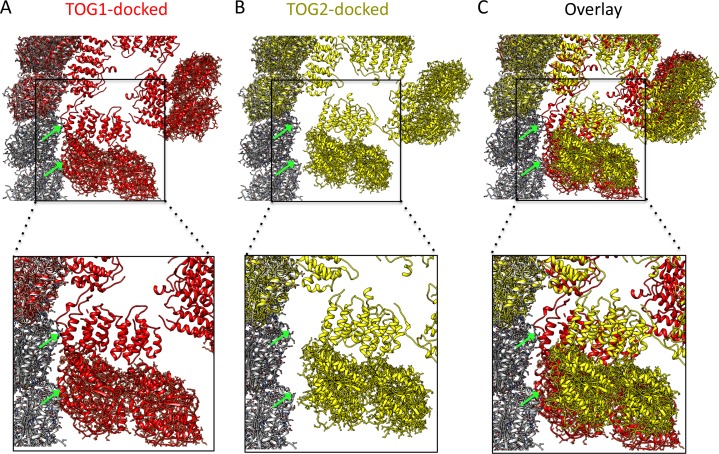
(A) Right, atomic model for four αβ-tubulin-bound TOG square X-ray structures (Figure 2) docked using αβ-tubulin bound to TOG1 at the terminal αβ-tubulin in a curved protofilament (PDB ID: 3RYH). Left, magnified view of the zone of steric contact between TOG2-αβ-tubulin in the second subunit and the penultimate αβ-tubulin of the protofilament below the polymerization site. (B) Right, atomic model for four αβ-tubulin-bound TOG square X-ray structure (Figure 2) docked using αβ-tubulin bound to TOG2 at the terminal αβ-tubulin in a curved protofilament (PDB ID: 3RYH). Left, magnified view of the zone shown in A between TOG1-αβ-tubulin in the second subunit and the penultimate αβ-tubulin of the protofilament. Details and overlay images are shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 1. (C) Docking the isolated TOG1-TOG2 two-αβ-tubulin assembly structure (extracted from the pseudo-dimer structure) onto the terminal αβ-tubulin of the curved protofilament. (D) Docking of the unfurled 1:2:1 unfurled assembly structure (Figure 5) to the curved protofilament revealing TOG1 to be positioned at the base of the new assembly while TOG2 is positioned at the outer end of the newly formed MT plus-end.