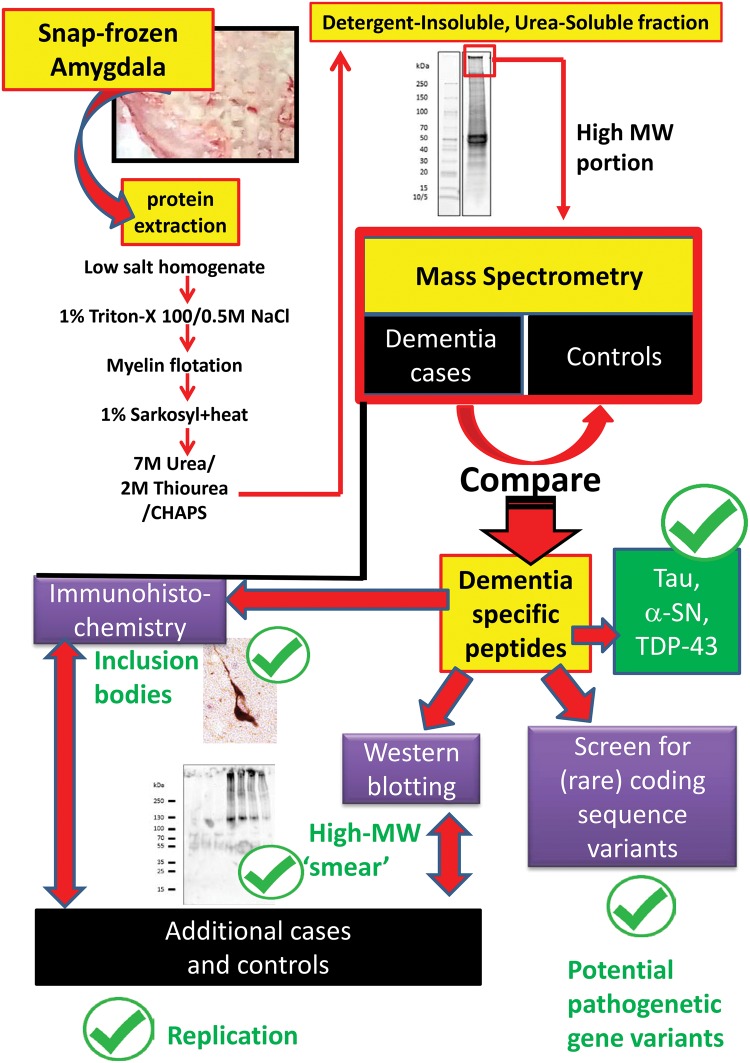
FIGURE 1.
Overview of study design and experiments performed in the current study. With the goal of identifying novel detergent-insoluble pathogenic proteins (DIPPs), experiments began with protein fractionation followed by comparison of high-molecular weight, urea-soluble (detergent-insoluble) proteins from cognitively impaired and control subjects. Optimally, a novel DIPP candidate would be more likely to be present in a preparation that was found to also contain established DIPPs: Tau, α-synuclein, and/or TDP-43. Downstream assessments included Western blots and immunohistochemistry, with separate replication, and with a preliminary genetic screen to evaluate whether rare coding variants could be identified that cosegregated with dementia-inducing disease phenotype.