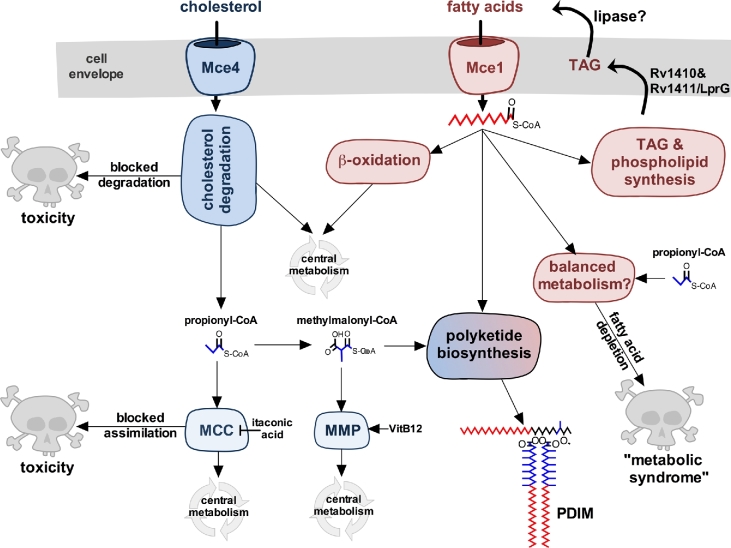
Figure 4.
Cholesterol and fatty acid utilization in M. tuberculosis. Cholesterol and fatty acid degradation fuels central metabolism and supplies pathways required for pathogenesis. Cholesterol-derived propionyl-CoA can be assimilated by the MCC or converted into methylmalonyl-CoA. Methylmalonyl-CoA can be assimilated by the MMP or used for polyketide lipid synthesis. Inactivating cholesterol degradation enzymes or the MCC can induce metabolic intoxication that inhibits bacterial growth. Salvaged fatty acids can also be used in biosynthetic reactions to generate membrane lipids, TAG and polyketide lipids. Cholesterol-derived propionyl-CoA induces a ‘metabolic syndrome’ that is associated with an inability to export TAG and/or when fatty acid pools are depleted. Vitamin B12 is indicated as VitB12.