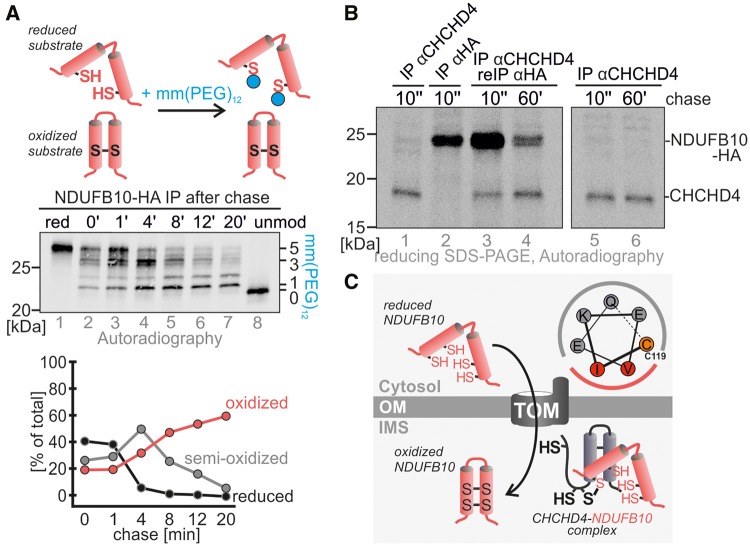
Figure 6.
CHCHD4 oxidizes NDUFB10 during maturation. (A) NDUFB10 forms two disulfide bonds during its maturation. Proteins were radioactively labelled, and followed for different chase times. After the chase proteins were modified with the alkylating agent mmPEG12 to distinguish reduced (i.e. modifiable) from oxidized protein. Then, NDUFB10 was isolated by immunoprecipitation and the precipitate analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. (B) CHCHD4 interacts with NDUFB10 during NDUFB10 maturation in pulse chase analysis. A denaturing immunoprecipitation against CHCHD4 was followed by a re-immunoprecipitation against NDUFB10, thus isolating CHCHD4-NDUFB10 complexes. Interaction between both proteins takes place very early during NDUFB10 maturation and is decreasing with time. (C) Model for maturation of NDUFB10 by CHCHD4. The potential CHCHD4 recognition motif in NDUFB10 allows for the initial interaction of NDUFB10 and CHCHD4. This motif is localized around cysteine 119. A mixed disulfide intermediate between both proteins is resolved once the disulfides in NDUFB10 are formed.