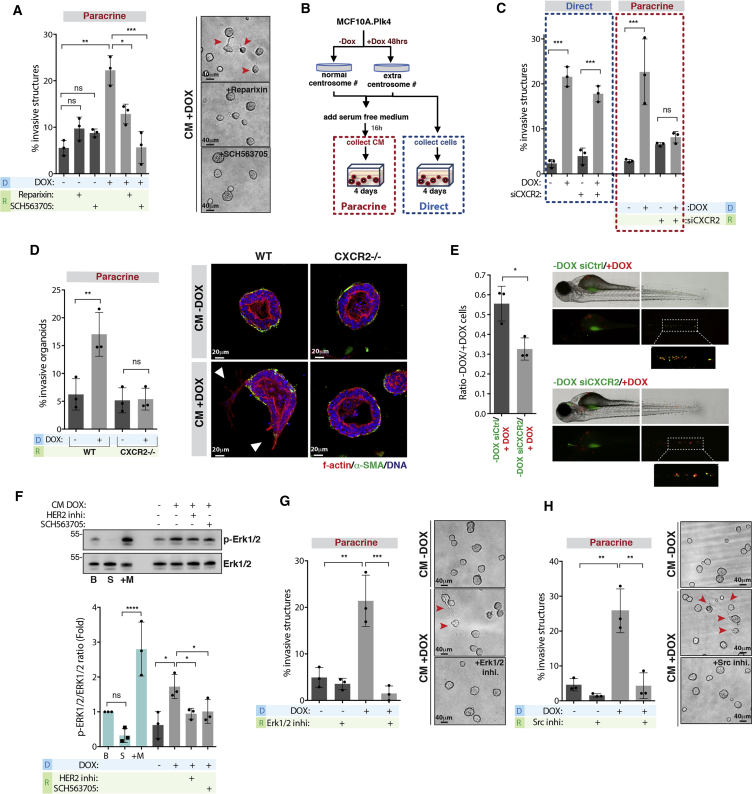
Figure 4.
Secreted IL-8 Is Crucial for Paracrine Invasion through Her2 Activation
(A) Left, quantification of invasive structures with and without the CXCR1/2 inhibitors Reparixin (100 nM) and SCH563705 (100 nM). Right, acinar structures. Red arrowheads indicate invasive acini. Scale bar: 40 μM.
(B) Experimental flowchart.
(C) Quantification of invasive structures upon CXCR2 depletion in cells with extra centrosomes (direct) or incubated with CM+DOX (paracrine).
(D) Left, quantification of invasive mammary organoids from WT or CXCR2−/− mice. Right, non-invasive and invasive mammary organoids. Scale bar: 20 μM.
(E) Left, ratio of disseminated cells in co-injection experiments. Right, zebrafish embryos co-injected with cells with (+DOX, red) and without centrosome amplification (−DOX, green). Number of injected fish co-injection control siRNA = 71; co-injection CXCR2 siRNA = 121.
(F) Top, levels of p-Erk1/2 and total Erk1/2 in cells. Bottom, ratio of phospho/total Erk1/2. B, basal conditions; S, serum starved cells; +M, serum starved cells after incubation with fresh medium.
(G) Left, quantification of invasive structures with or without Erk1/2 inhibitor (PD98059, 20 μM). Right, acinar structures. Red arrowheads indicate invasive acini. Scale bar: 40 μM.
(H) Left, quantification of invasive structures with and without Src inhibitor (PP2, 5 μM). Right, acinar structures. Red arrowheads indicate invasive acini. Scale bar: 40 μM.
For all graphics, error bars represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ns not significant.
See also Figure S4.