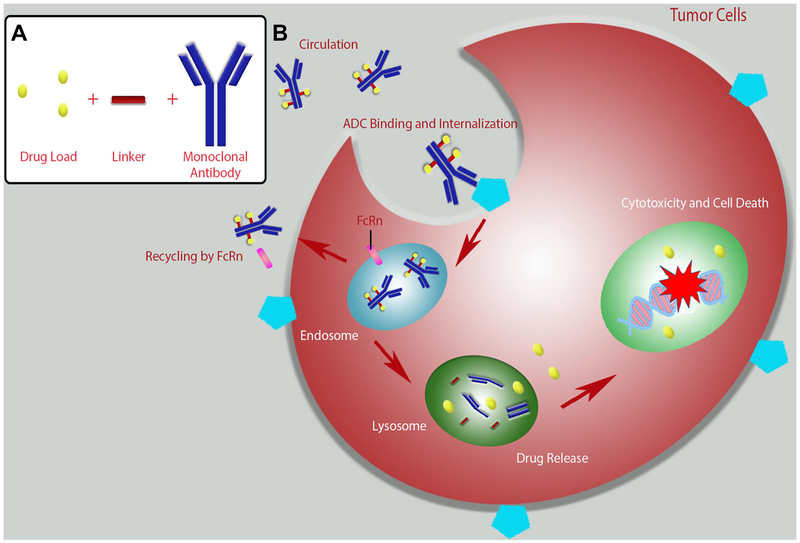
Fig. 2.
Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) assembly and interaction with target cells. a Assembly of an ADC. b Typical mechanism of action of an ADC. The administered ADC binds to antigens expressed on the surface of target tumor cells. Following binding, the ADC is internalized. Some of the ADC is recycled back to circulation by the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). The remainder of the ADC is trafficked from the late endosome to the lysosome where the antibody is degraded and the linked drug is released. The free drug enters the nucleus of the cell and damages DNA leading to cell death