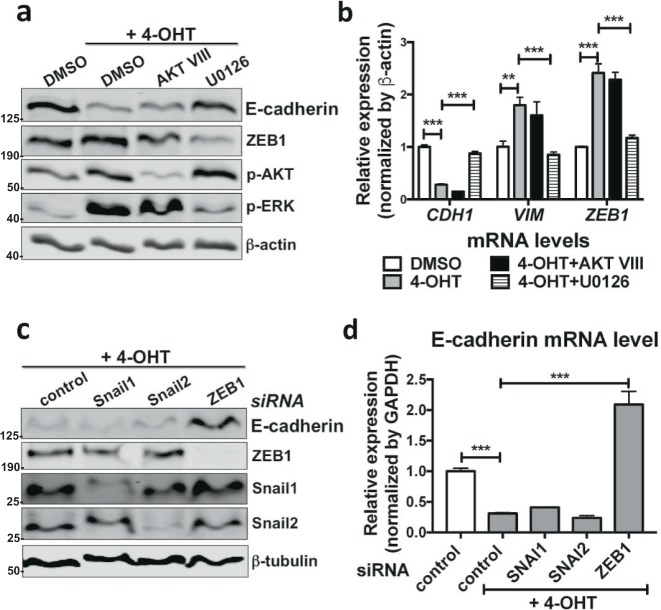
Fig. 3.
Activation of the RAS pathway drives EMT via ERK–ZEB1 in ATII cells. a Protein expression of E-cadherin, ZEB1, phospho-AKT (p-AKT) and phospho-ERK (p-ERK) in ATIIER:KRASV12 treated with 250 nM 4-OHT in the absence or presence of inhibitors AKT VIII (10 μM) or U0126 (10 μM) for 24 h. DMSO was used as a vehicle control and β-actin was used as a loading control. b Fold change in mRNA levels of CDH1 (E-cadherin), VIM (Vimentin) and ZEB1 in ATIIER:KRASV12 treated with 250 nM 4-OHT in the absence or presence of inhibitors AKT VIII (10 μM) or U0126 (10 μM) for 24 h. DMSO was used as a vehicle control. GAPDH-normalised mRNA levels in control cells were used to set the baseline value at unity. Data are mean ± s.d. n = 3 samples per group. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001. c Protein expression of E-cadherin, ZEB1, Snail1 and Snail2 in ATIIER:KRASV12 cells transfected with the indicated siRNA followed by treatment of 250 nM 4-OHT for 24 h. β-tubulin was used as a loading control. d Fold change in the mRNA level of CDH1 (E-cadherin) in ATIIER:KRASV12 cells transfected with the indicated siRNA followed by treatment of 250 nM 4-OHT for 24 h. GAPDH-normalised mRNA levels in control cells were used to set the baseline value at unity. Data are mean ± s.d. n = 3 samples per group. ***P < 0.001