Figure 4. A1R-D1R heteromer expression in mouse spinal cord motoneurons.
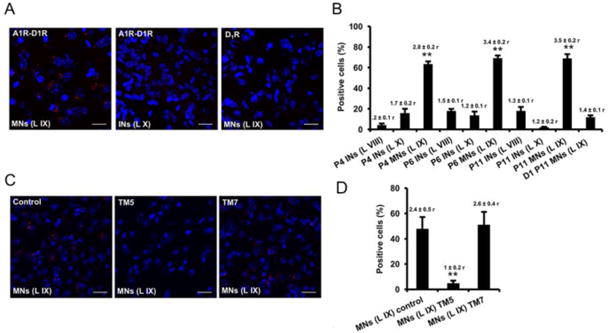
In situ proximity ligation assays were performed using slices from mouse lumbar spinal cord from P4, P6 and P11 animals. Slices from lamina IX (motoneurons) and laminae VIII and X (interneurons) were analyzed using specific primary antibodies directed against A1R and D1R (A1R-D1R) or only against D1R as negative control (D1). Slices were treated for 4 h with vehicle (A, B and control in C and D) or with 4 μM of D1R TM 5 or TM7 peptides (C, D). In (A and C), confocal microscopy images (superimposed sections) from (A) laminae IX and X from P11 animals in which heteromers appear as red spots in lamina IX, but not in lamina X or in negative controls, and from (C) lamina IX from P5 animals in which heteromers appear as red spots in non peptide treated slices (control) and treated with D1R TM 7 but not in slices treated with TM5. In all cases, cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 20 μM. In (B and D) the percentage of cells showing red spots related to the total cell number determined as stained blue nuclei is given in each case as well as the ratio (r) between the number of red spots and cells showing spots (top columns). Values are mean ± S.E.M. of n =7-15. **: p < 0.01 as compared with the negative control D1 in (B); ** p < 0.01 as compared with the control non-treated with peptides in (D) (one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's comparisons).
