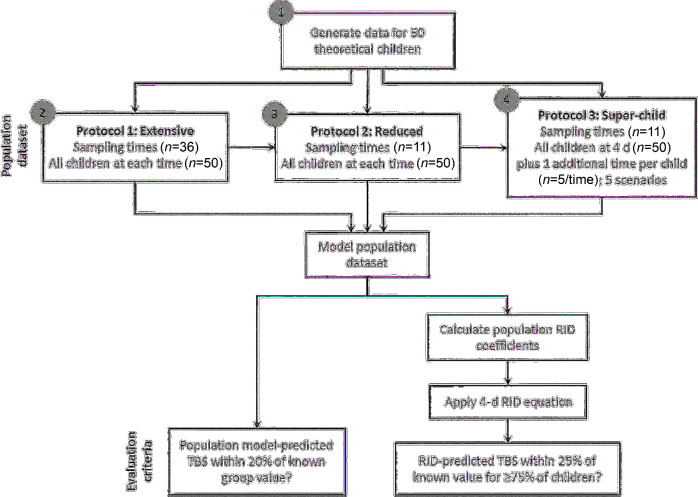
FIGURE 1.
Flow chart of the theoretical analysis used to evaluate the super-child approach. A database for 50 theoretical children with known values for vitamin A TBS and other variables was used to generate population (mean) data sets for 3 sampling protocols. For each data set, model-based compartmental analysis was applied to estimate vitamin A TBS and retinol kinetics for the group. Population estimates for RID equation coefficients were calculated from the model and used to predict vitamin A TBS at 4 d for individual subjects. Predictions of TBS were compared with known values using the specified evaluation criteria. Circled numbers correspond to the following objectives: 1) use model-based compartmental analysis to generate a database of known values for theoretical subjects that was needed to test the population-based approach, 2) establish proof-of-concept that population-based modeling of a detailed data set provides accurate estimates for the variables of interest, 3) validate the approach using reduced sampling times, and 4) validate the super-child design being implemented in ongoing super-child studies. RID, retinol isotope dilution; TBS, total body stores.