Figure 1.
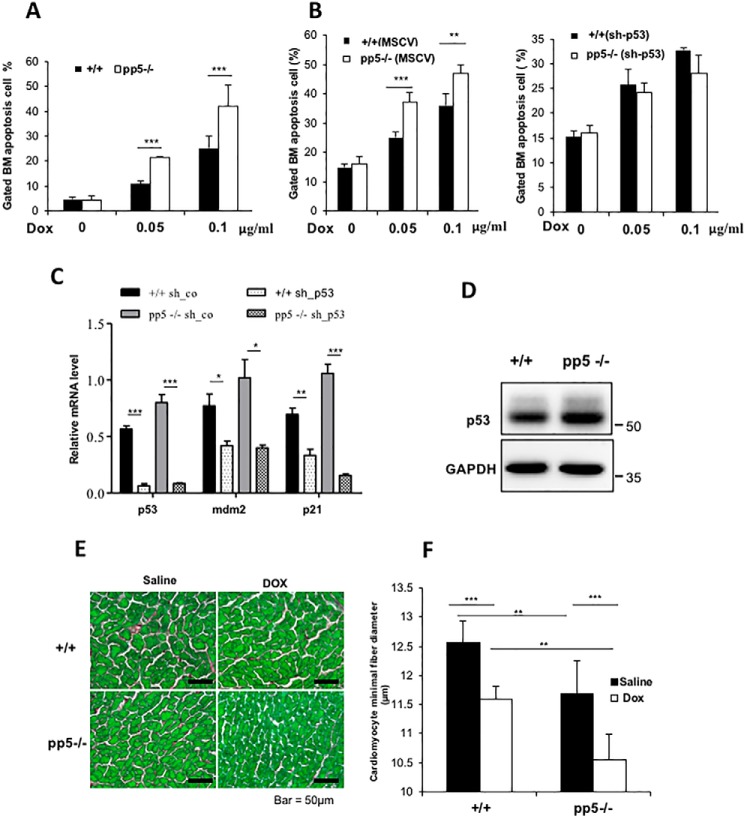
Characterization of WT and PP5 KO mice after saline or DOX treatment. A, ablation of PP5 gives rise to bone marrow cells that are sensitive to p53-dependent apoptosis. WT and PP5 KO bone marrow (BM) cells were treated with DOX (0.05 and 0.1 μg/ml) for 12 h and then stained with annexin V and propidium iodide. Apoptotic cells (annexin V–positive cells) are indicated as a percentage of gated cells. Apoptotic cells are included in the graphical representation, which represents three independent experiments. B, WT and PP5 KO bone marrow low-density mononuclear cells were isolated and transduced with pMSCV or pMSCV-sh-p53. Following transduction, cells were sorted for eGFP using FACS to enrich for transduced cells, treated with DOX for 12 h, and analyzed by flow cytometry. C, real-time quantitative RT-PCR revealed that the expression of p53 and its downstream targets MDM2 and p21 decreased after sh-p53 transduction. sh-co, control. D, Western blot analysis showed the p53 expression levels in WT and PP5 KO bone marrow. E, sections from saline- or doxorubicin-treated WT and PP5 KO hearts stained with Sirius Red/Fast Green (scale bars, 50 μm).cardiomyocyte F, cardiomyocyte minimal fiber diameter (μm) measurements in WT and PP5 KO mice treated with saline or DOX. Values are presented as the mean ± S.D. (error bars) using Student's t test. * represents p < 0.05, ** represents p < 0.01, and *** represents p < 0.001.