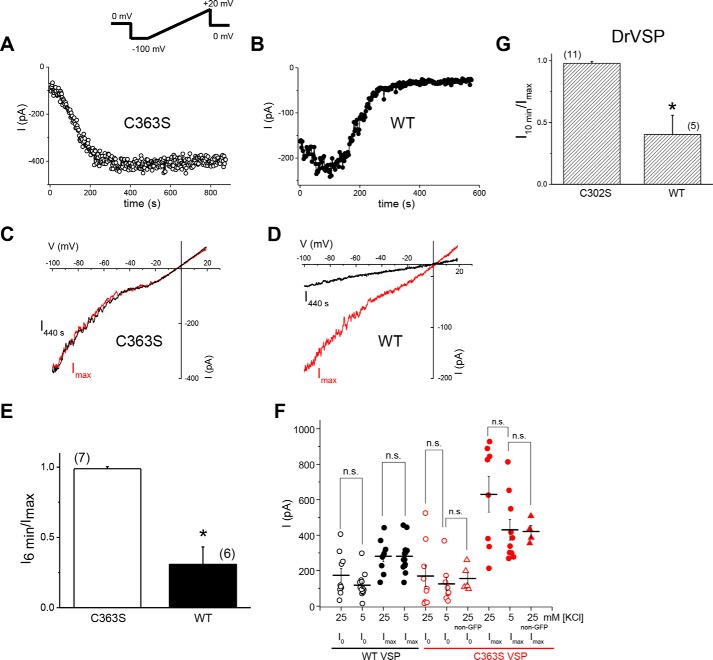
Figure 6.
Voltage dependence of VSP effect on native TRPM7 channels. A–D, time courses of inward TRPM7 current (A and B) and I–V (C and D) in DVF Cs+-based bath solutions. Voltage ramps from −100 to +20 mV were applied. Data were obtained from HEK cells expressing WT or C363S CiVSP. E, current remaining after 6 min of whole-cell recording, divided by the maximum current attained in the respective cell. Inward current at −100 mV was plotted. Internal free [Mg2+] was 10 μm. *, p < 0.05. F, cells transfected with WT or C363S CiVSP were grown in RPMI 1640 medium containing 5.3 mm KCl or 25.3 mm KCl. Shown are TRPM7 current amplitudes at break-in and maximum currents attained. Current measurements taken from non-GFP cells among the C363S VSP–transfected cells were used as an untransfected control. Pairs grown in high and low K+ were not significantly different for WT and C363S VSP (t test, p > 0.05). [Mg2+]i = 400 nm. The holding potential was −60 mV. n.s., not significant. G, TRPM7 current decay in C302S- and WT DrVSP–transfected cells. Shown is current remaining after 10 min of recording divided by the maximum current. −100 to +20 mV ramps were used as in A–E. The internal free [Mg2+] was 10 μm, and the external DVF solutions was Na+-based. The holding potential was 0 mV. *, p < 0.05.