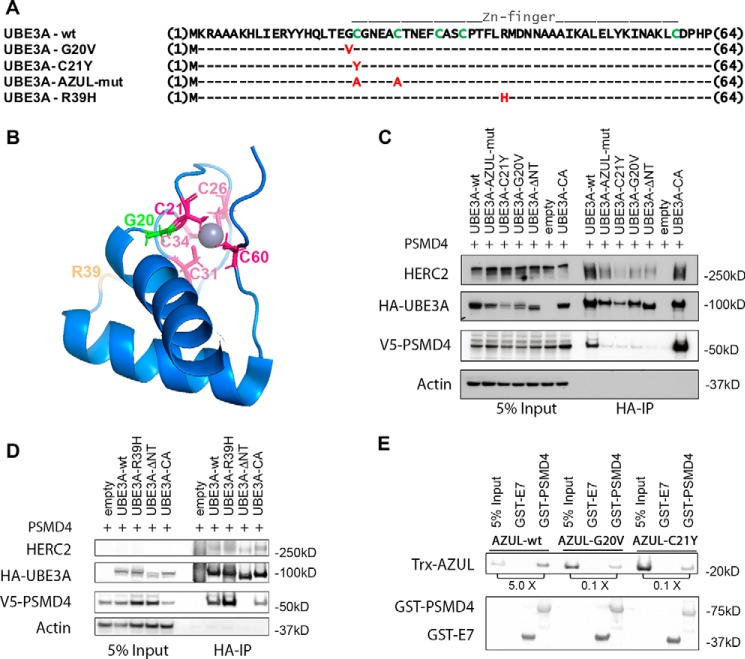
Figure 3.
Mutations in the AZUL domain of UBE3A affect binding to PSMD4. A, sequence alignment of UBE3A-WT and AZUL domain mutants. G20V and C21Y represent point mutations identified in Angelman patients. In the AZUL mutant, two Zn2+-coordinating cysteine residues were exchanged to alanine to affect AZUL structure (note that this mutant additionally carries the C820A mutation in the HECT domain, rendering it ligase-inactive). R39H represents a presumably benign point mutation identified in an Angelman patient with an additional frameshift mutation. B, NMR structure of the UBE3A AZUL domain shows localization of Zn2+-coordinating cysteine residues (pink), the glycine mutated in the G20V AS mutant (green), and the arginine mutated in the putative benign R39H mutation (orange). C and D, HEK293T cells were transfected with V5-tagged PSMD4 and HA-tagged UBE3A of the different N-terminal UBE3A mutants or empty vector. Prior to harvesting, cells were treated for 4 h with 300 nm bortezomib. Cells were lysed 24 h after transfection, and HA-tagged proteins were precipitated using HA-agarose beads. 5% of the lysate used for immunoprecipitation was used as input. Precipitated proteins were detected by Western blot analysis using anti-HA and anti-V5 antibodies, respectively. E, GST pulldown assay using recombinant bacterially expressed GST-PSMD4 and GST-HPVE7 (negative control) and recombinant bacterially expressed Trx-tagged AZUL domain (WT, G20V, and C21Y variants). GST-proteins were precipitated using GSH-Sepharose. The ratio of pulled down Trx-AZUL domain proteins to 5% input is indicated. AZUL-WT directly interacts with PSMD4, whereas the AZUL(G20V) and AZUL(C21Y) variants showed significantly impaired binding to PSMD4.