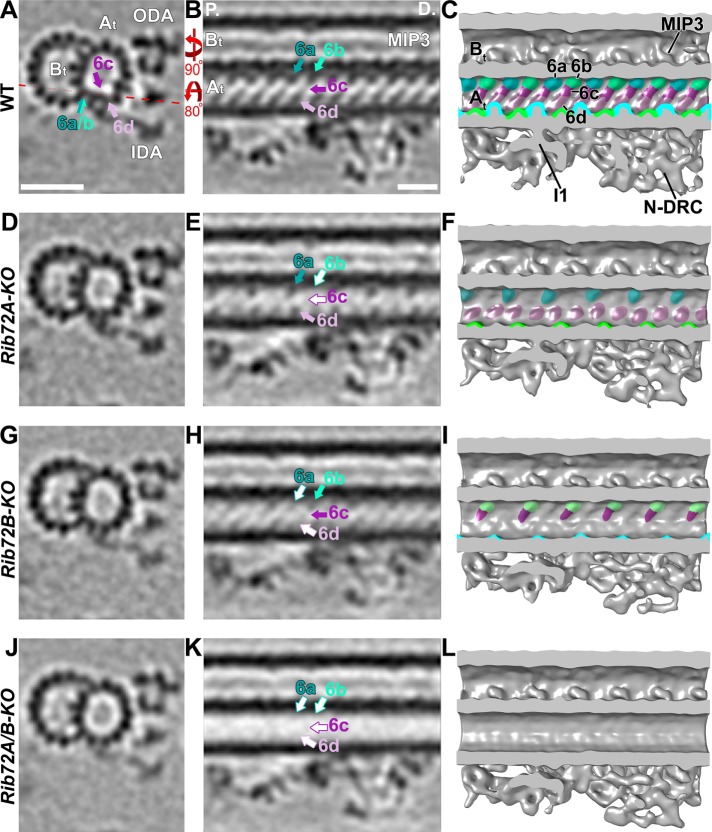
FIGURE 7:
Loss of RIB72A/B affects the MIP6 structure and shows that MIP6 is composed of multiple subunits. (A–L) Tomographic slices (A, B, D, E, G, H, J, K) and isosurface renderings (C, F, I, L) in cross-sectional (A, D, G, J; from proximal) and longitudinal bottom view (B, C, E, F, H, I, K, L; proximal on the left) of Tetrahymena axonemal repeat units. RIB72A-KO (D–F), RIB72B-KO (G–I), and the double mutant (J–L) each have defects in the MIP6 structures (6a, teal; 6b, aqua; 6c, purple; 6d, mauve) as compared with WT (A–C); missing structures are indicated by open arrows outlined by the respective colors for MIP6 subunits. The RIB72A mutant lacked MIP6b (aqua arrow) and MIP6c (purple arrow), whereas the RIB72B mutant was missing only MIP6a (teal arrow) and MIP6d (mauve arrow). The defects in the double KO were additive, that is, all four MIP6 subunits were missing. Red dotted line in A indicates slice position of longitudinal tomographic slices, for example, in B. Other labels: At, A-tubule; Bt, B-tubule; I1, I1 dynein; IDA, inner dynein arms; MIP3; N-DRC, nexin dynein regulatory complex; ODA, outer dynein arms. Scale bars: 25 nm (A, valid also for D, G, J), 16 nm (B, valid also for E, H, K).