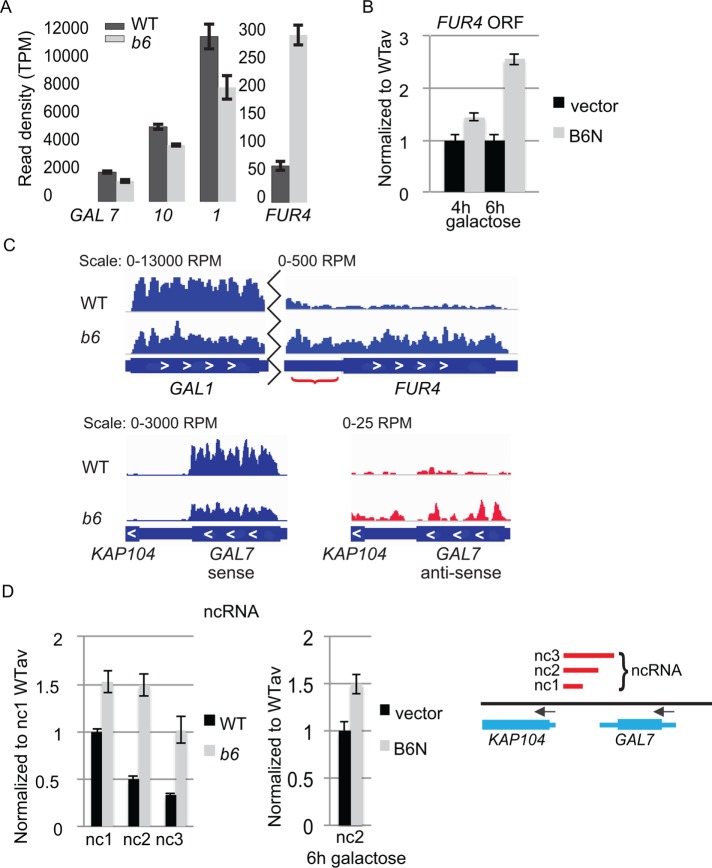
FIGURE 4:
brr6-1 and the NLS-Brr6N fragment perturb coding and noncoding transcription at the FUR4-GAL1,10,7 gene region. (A) RNAseq results comparing transcript levels (read density [transcripts per million, TPM]) for GAL7, GAL10, GAL1, and FUR4 in WT (wild type, yPH399) vs. b6 (brr6-1, yDBK168). (B) RT-qPCR measurement of FUR4 ORF transcripts in wild-type cells (W303) carrying vector (pJL602) vs. the B6N (pPGAL_NLS-BRR6N) construct. (C) Bar plot of RPM-normalized aligned sense (blue) reads for GAL1 and FUR4 coding and intergenic regions (red bracket) and sense and antisense (red) reads for GAL7 (representative replicates). (D) DN9 primed RT-qPCR of ncRNA (nc1, 2, and 3) transcripts in WT (wild-type, yDBK165) and b6 (brr6-1, yDBK166) cells (left) and the nc2 transcript in wild-type cells (W303) carrying vector (pJL602) vs. the B6N (pPGAL_NLS-BRR6N) construct (middle). Amplicons (GAL nc1-3) are indicated by red bars in the region from KAP104 to GAL7 (right). qPCR data were normalized and expressed as in Figure 2. Error bars (SEM) reflect ≥3 biological replicates.