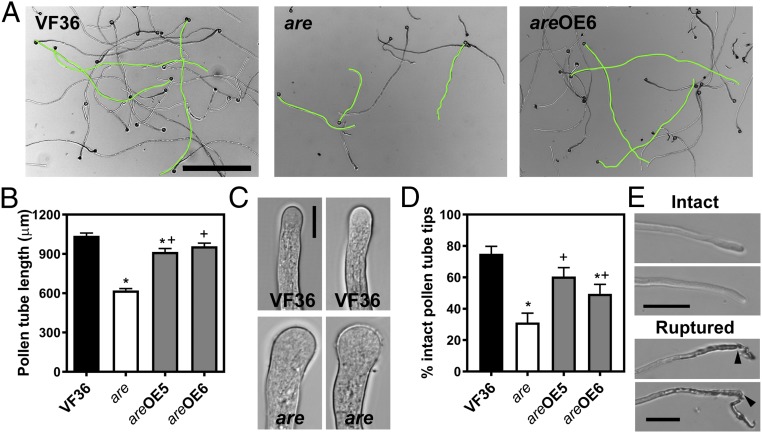
Fig. 3.
Flavonols regulate pollen tube growth and integrity in tomato. (A) Bright-field images of VF36, are, and are-35S:F3H complementation line #6 pollen tubes grown in vitro for 4 h. (Scale bar, 500 µm.) Several pollen tubes of each phenotype are highlighted in green. (B) Quantification of in vitro pollen tube length after 4 h of growth in VF36, are, and are-35S:F3H complementation lines. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. n = 127–140 tubes measured across three independent experiments. (C) Bright-field images of pollen tube tips. (Scale bar, 10 µm.) (D) Quantification of pollen tubes with burst tips in VF36, are, and are-35S:F3H complementation lines after 4 h of pollen tube growth. Data are mean ± SEM. (B and D) Asterisks indicate significant differences between VF36 and other genotypes and plus signs indicate differences between are and complementation lines, according to an ANOVA followed by a Šídák post hoc test with P < 0.05. (E) Bright-field images illustrate pollen tubes with intact and ruptured tips. Black arrows indicate points of rupture at the pollen tube tip. (Scale bars, 50 µm.)