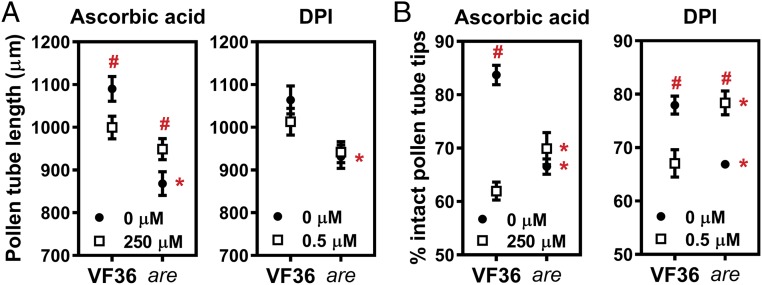
Fig. 6.
Antioxidant treatment and inhibition of ROS synthesis rescue defects in pollen tube growth and integrity caused by reduced flavonol levels. (A) Quantification of in vitro tube growth in VF36 and the are mutant grown for 4 h at 28 °C. Supplementation of the pollen germination medium with the nonenzymatic antioxidant ascorbic acid or the NADPH oxidase inhibitor DPI occurred after 90 min of growth. Data represent mean ± SEM. n = 80 tubes measured across two independent experiments. (B) Quantification of pollen tube integrity in VF36 and the are mutant. Data originate from the same pollen samples as in Fig. 5A, but have different solvent controls, as outlined in the methods. Data represent mean ± SEM. The error bar is shorter than the height of the symbol for tube integrity in the are mutant treated with 0 µM DPI. Integrity was assessed in more than 150 pollen tubes for each condition and genotype across two independent experiments. In A and B, asterisks indicate significant differences between VF36 and are within the same concentration of ascorbic acid or DPI, and pound signs highlight differences between concentrations within the same genotype, according to two-way ANOVA followed by a Fisher’s LSD test with P < 0.05.