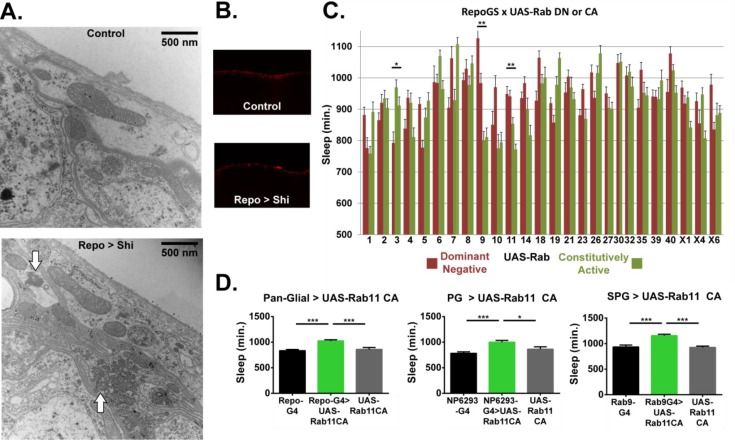
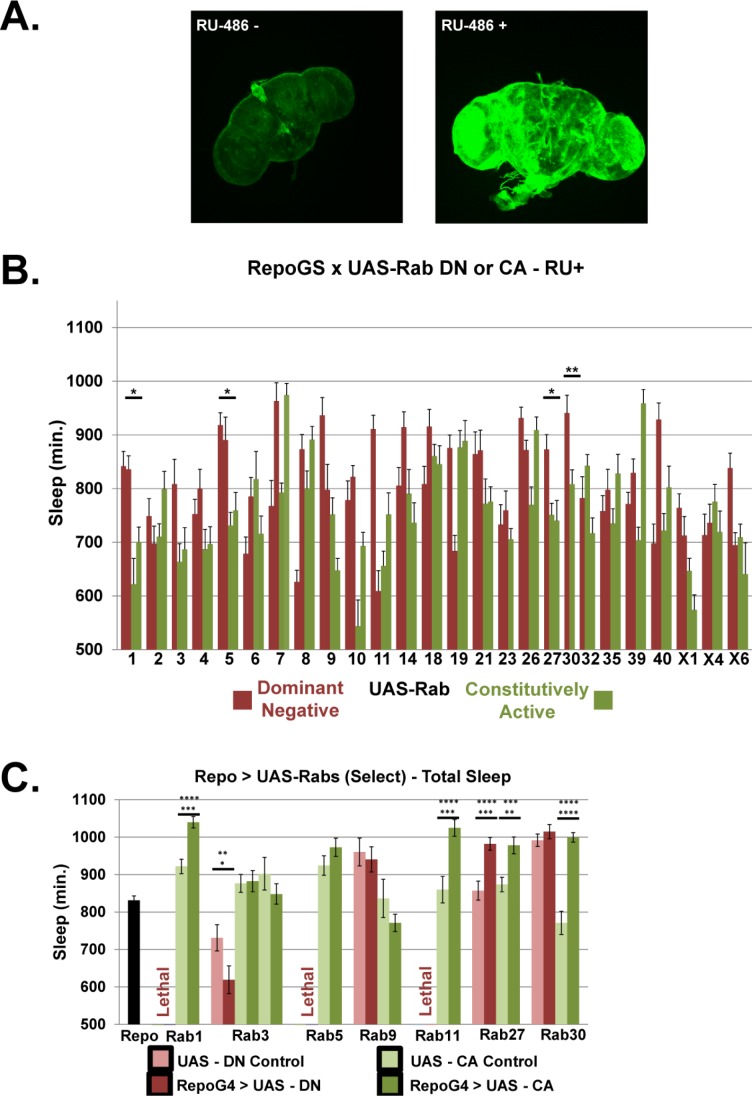
Figure 4. Ultrastructural morphology and genetic analysis of Rab proteins support a sleeprelevant function of vesicle trafficking in surface glia.
(A) Transmission electron micrographs of surface glia of individual Repo-GAL4 > UAS-20xShi.ts1 and Control female fly brains. Perineurial glia are the most superficial layer with subperineurial glia appearing as the generally thinner and darker layer immediately basal to the perineurial glia. White arrows indicate presence of microtubule bundles. (B) External aspect of hemolymph-brain barrier visualized by injection and fixation of Alexa647-10kd dextran in Repo-GAL4 > USA-20xShi.ts1 and control brains, demonstrating an intact barrier in both genotypes. (C) Total sleep time of RepoGS > UAS Rab CA or DN flies, in the absence of RU486. Red bars represent UAS-Rab DN and green bars are UAS-Rab CA, with two insertions available in most cases (n = 7–16, for all genotypes). Significant Rabs are those in which all DN lines were consistently and significantly different from all CA lines measured by one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak post-hoc test or unpaired t-test for Rab30, with *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Displayed significance value represents the largest p-value of the 3–4 comparisons. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). (D) Total sleep time of flies expressing Rab11 CA in all glia (Repo-GAL4), perineurial glia (NP6293-GAL4), and subperineurial glia (Rab9-GAL4) as compared to GAL4 and UAS controls (n = 15–30), statistics as above.