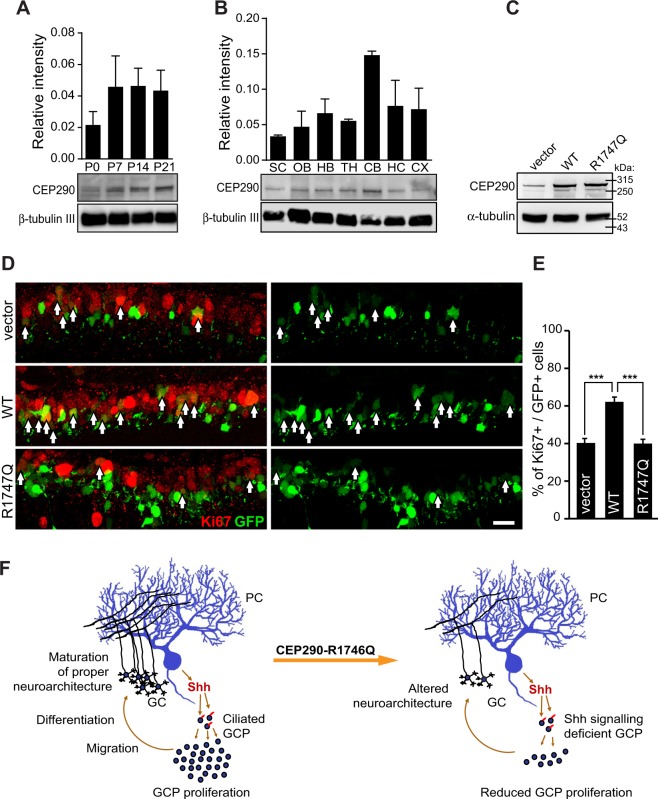
Figure 6.
Cep290-R1747Q fails to maintain GCPs in the proliferative state during cerebellar development. Immunoblotting analysis of Cep290 protein expression in mouse whole brain lysate harvested (A) at indicated postnatal days (P) or (B) in indicated brain regions harvested from P14 pups. Bar graphs show Cep290 protein abundance quantified as intensity of Cep290 bands relative to reference protein (β-tubulin III) (three independent experiments). See also Fig. S4D–G for full blots. SC = spinal cord, OB = olfactory bulb, HB = hind brain, TH = thalamus, CB = cerebellum, HC = hippocampus, CX = cortex. (C) HEK293T cells transfected with pCIG2, pCIG2-Cep290 or pCIG2-Cep290-R1747Q constructs. Both pCIG2-Cep290 and pCIG2-Cep290-R1747Q showed elevated Cep290 expression at a similar level. (D) Immunostaining of the cell cycle marker Ki67 in mouse cerebellar slices electroporated with pCIG2, pCIG2-Cep290 or pCIG2-Cep290-R1747Q constructs at P6. Ki67+ (red) cell among electroporated cells, which also express EGFP (green) are indicated with arrows. Scale bar = 20 μm. (E) The bar graph shows an increased percentage of Ki67+ GCPs in cerebella electroporated with pCIG2-Cep290 (n = 4 animals) but not pCIG2-Cep290-R1747Q (n = 6 animals) compared to the pCIG2-vector control (n = 7 animals). ***p < 0.001, One-way ANOVA. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. (F) Working model of CEP290-R1746Q mediated alteration in the neurodevelopment of the cerebellum. In the neurotypical brain, Shh secreted by Purkinje cells (PC) are sensed by ciliated GCPs and results in expansion of the progenitor pool and the consequent establishment of the proper cerebellar neurocircuitry. However, GCPs expressing the dominant negative CEP290-R1746Q variant are defective in their response to the Shh morphogen thus resulting in a diminished GCP population and consequent neuroarchitectural alterations.