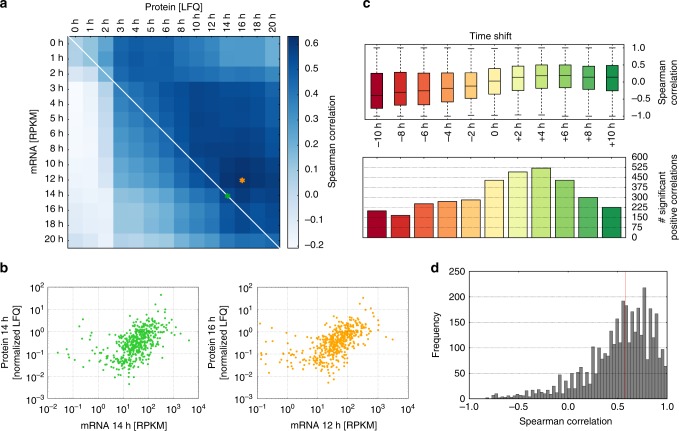
Fig. 2.
Limited correlation between mRNA and protein levels. a Global RNA−protein correlation across all samples. Heatmap of Spearman correlation coefficients between protein abundance (x-axis; quantified using MaxLFQ), and mRNA levels (y-axis; expressed as RPKM values), at the same (diagonal) or shifted (off-diagonal) time points of embryonic development. Only the top 500 proteins showing largest absolute fold-changes compared to the 0 h time point were considered. Green and orange stars indicate maximum correlation between same and shifted time points, respectively. Corresponding scatter plots are shown in (b). b Maximum global RNA−protein correlation. Scatter plots showing correlation of mRNA (RPKM) and protein (LFQ) levels at 14 h (left, ρ = 0.56), or between mRNA at 12 h and protein at 16 h (right, ρ = 0.63). Chosen time points correspond to the orange and green stars marked in (a). c Local correlations relating the mRNA and protein time courses of individual genes were calculated using the Spearman correlation coefficient. Boxplots indicate the distribution of Spearman correlation coefficients for all 3761 mRNA−protein pairs (black line: median; boxes: quartiles; whiskers: 95-percentile) (upper panel). Time shifts between mRNA and protein dynamics were introduced by adding a constant to the time axis of the protein (0 h: no shift). Positive and negative values reflect that protein lags behind or is advanced relative to its mRNA, respectively. Number of mRNA−protein pairs with a significant (Student’s t test, two-sided, p < 0.05), positive correlation for each time shift (bottom panel). d Distribution of maximum Spearman correlation coefficients across all time shifts. For each individual mRNA−protein pair (n = 3761), the maximum correlation between the mRNA and protein time courses at any time shift between 0 h and +10 h was determined and considered in this histogram. The red line indicates the median of all correlation coefficients