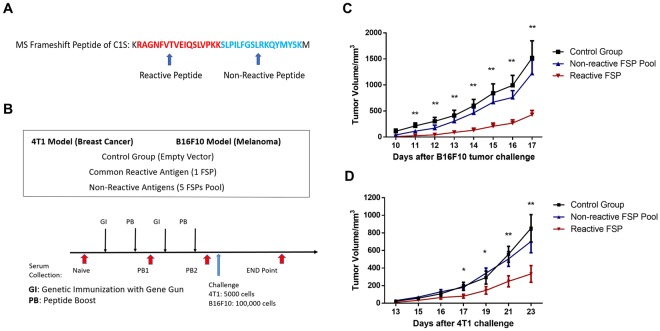
Figure 4.
Reactive FSPs showed protection in the mouse melanoma and breast cancer models. (A) Reactive and non-reactive FSPs from the same microsatellite frameshift antigen of C1S. (B) 3 groups of mice were used: the control group was immunized with control plasmid, non-reactive FSPs pool and reactive FSP. All 3 groups received 2 rounds of genetic immunization with gene gun and peptide boost via subcutaneous injection. The B16F10 cell line was used for the melanoma model and the 4T1 cell line was used for breast cancer model. Each group had 10 mice. (C) Reactive FSPs slowed tumor growth significantly compared to the non-reactive FSPs pool and the control group in the melanoma model (student’s t-test, p-value < 0.01), error bar represented mean ± SEM. (D) The Reactive FSPs offered tumor protection in mouse breast cancer model as well. The tumor volume was significantly lower than control group and non-reactive FSPs pool group (student’s t-test, p-value < 0.05).