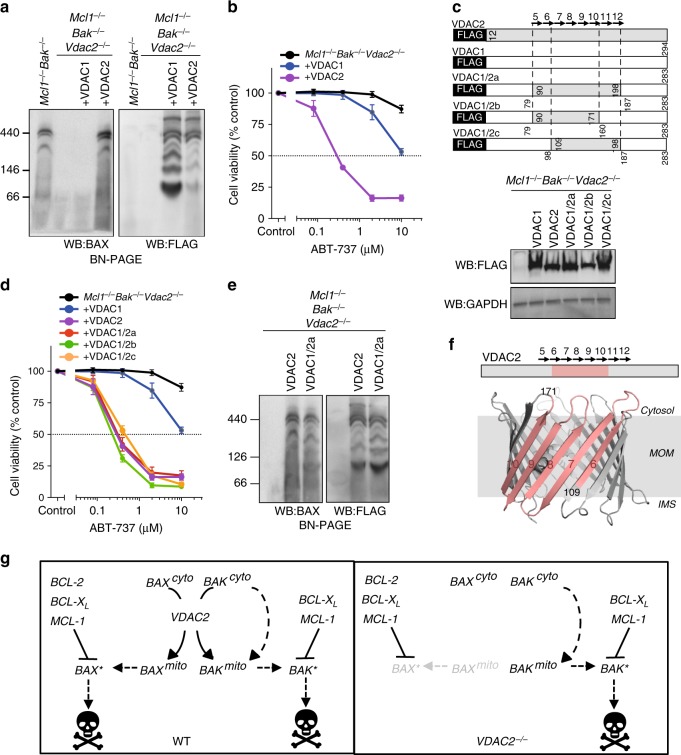
Fig. 3.
Interaction with VDAC2 is important for BAX apoptotic function. a BAX mitochondrial complex formation specifically relies on VDAC2. Mitochondria-enriched fractions from Mcl1−/−Bak−/−Vdac2−/− MEFs reconstituted with FLAG-mVDAC1 or FLAG-hVDAC2 were analyzed by BN-PAGE and immunoblotted for BAX (left) or FLAG to detect ectopically-expressed VDACs (right). b BAX apoptotic function relies on VDAC2. Cells as in (a) were treated with ABT-737 and cell viability was assessed. c–e Rescue of BAX apoptotic function correlates with interaction with a specific region of VDAC2. Mcl1−/−Bak−/−Vdac2−/− MEFs stably expressing FLAG-mVDAC1/hVDAC2 chimeras (c) were analyzed for expression by immunoblotting for FLAG (or GAPDH as a loading control), cell viability following treatment with ABT-737 (d), and complex formation by BN-PAGE and immunoblotting for BAX or FLAG (e). f BAX interacts with a defined region of VDAC2. Interaction of BAX requires aa109-171 of hVDAC2 (salmon) mapped onto the structure of zebrafish VDAC2 (PDB 4BUM64). MOM mitochondrial outer membrane, IMS intermembrane space. g VDAC2 is essential for BAX, but not BAK to target mitochondria and mediate apoptosis. In wild-type cells, cytosolic BAX (BAXcyto) relies on VDAC2 to associate with mitochondria (BAXmito) and activate (BAX*). In the absence of VDAC2, BAX cannot drive cell death. Although the ability of BAK to associate with mitochondria is also perturbed in VDAC2−/− cells14, 31, sufficient BAK can still target mitochondria through a VDAC2-independent mechanism to drive apoptosis. Data presented in (b) and (d) is mean+/− SEM of three independent experiments