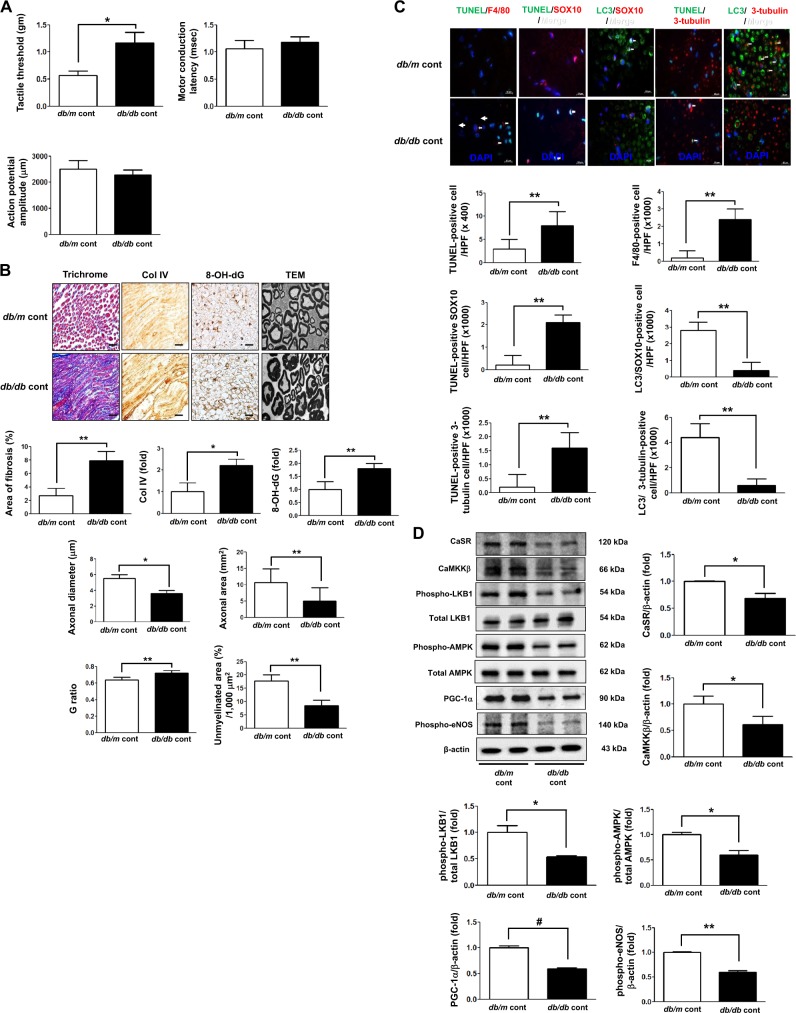
Fig. 8. Functional and phenotypic changes in the sciatic nerve of 8-week-old db/m and db/db mice.
a Effects of cinacalcet on the tactile threshold, motor conduction latency, and action potential amplitude were determined. b Nerve fibrosis (Masson’s trichrome and Col IV), oxidative stress (8-OH-dG), and the axonal diameter and area, the G ratio, and area of unmyelinated fiber in the sciatic nerves were determined. Representative electron microscopic images of the sciatic nerve bundles (×5000) are shown. Scale bars represent 2 μm. c Immunofluorescences for TUNEL, F4/80-positive cells, TUNEL-SOX10- and TUNEL-β3 tubulin-positive cells, and LC3-SOX10- and LC3-β3 tubulin-positive cells were determined. The white arrows indicate TUNEL-SOX10- and TUNEL-β3 tubulin-positive cells and LC3-SOX10- and LC3-β3-tubulin-positive cells, respectively. The quantitative analyses of the results are shown (c, original magnification, ×1000). Scale bars represent 10 μm (b, c). (n = 6 independent experiments in each experiments) *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the db/m cont group. d The expression levels of CaSR, CaMKKβ, phospho-Ser428 LKB1, phospho-Thr172 AMPK, PGC-1α, phospho-Ser1177 eNOS, Bcl-1, and β-actin of the sciatic nerve were determined. Representative western blot of CaSR, CaMKKβ, phospho-Ser428 LKB1, phospho-Thr172 AMPK, PGC-1α, phospho-Ser1177 eNOS, and β-actin and quantitative analyses of the results are shown (d). (n = 4 independent experiments in each experiments) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and #p < 0.001 compared with the other groups