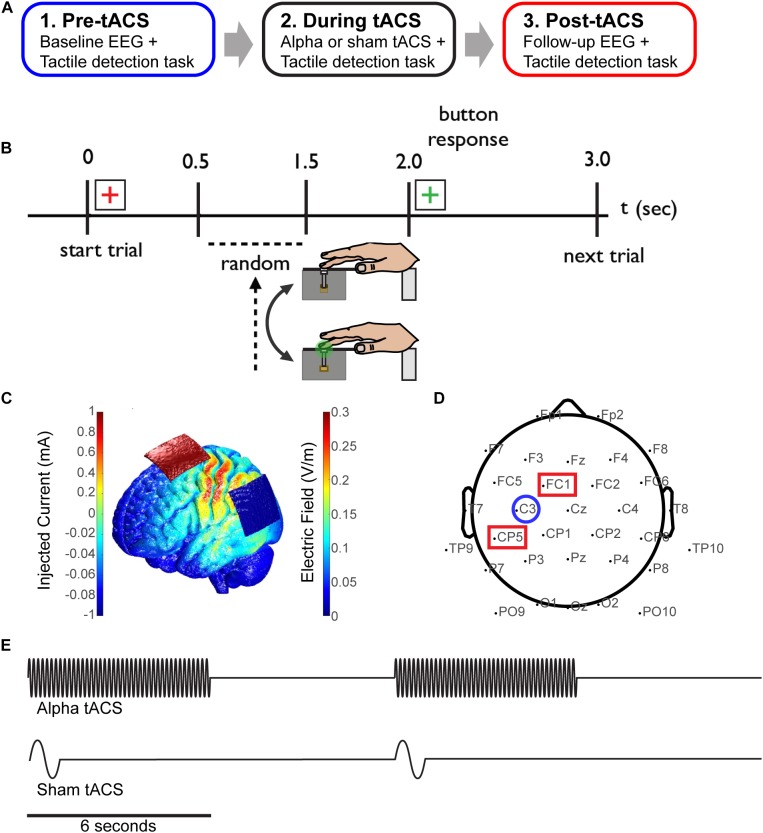
FIGURE 1.
Combining EEG and tACS during a tactile detection task. (A) The experimental session was divided into three time blocks; pre-, during and post-tACS (sham or alpha). (B) Schematic of the tactile detection task. Participants rested their right hand on a tactile stimulator that delivered brief light taps to the finger (third digit) at perceptual-threshold level, and subsequently reported detection of the stimulus using their left hand. A red cross-hair cued the start of the trial, and a green crosshair cued participants to subsequently select a response. (C) Finite element modeling was used to determine a stimulation montage resulting in maximal current flow over somatosensory cortex (see “Materials and Methods”). (D) Simultaneous EEG-tACS set-up. Stimulating electrodes were placed over CP5 and FC1 (red squares; International 10–20 system), and data was analyzed from EEG electrode C3 (blue circle), overlying primary somatosensory cortex. (E) Schematic of the alpha and sham tACS protocols. Electrical stimulation was applied at participants’ individual alpha frequency at 1 mA for a period of 6 s on/off (alpha tACS, top), or was ramped up to 1 mA at 1 Hz for 1 cycle and then turned off (sham tACS, bottom).