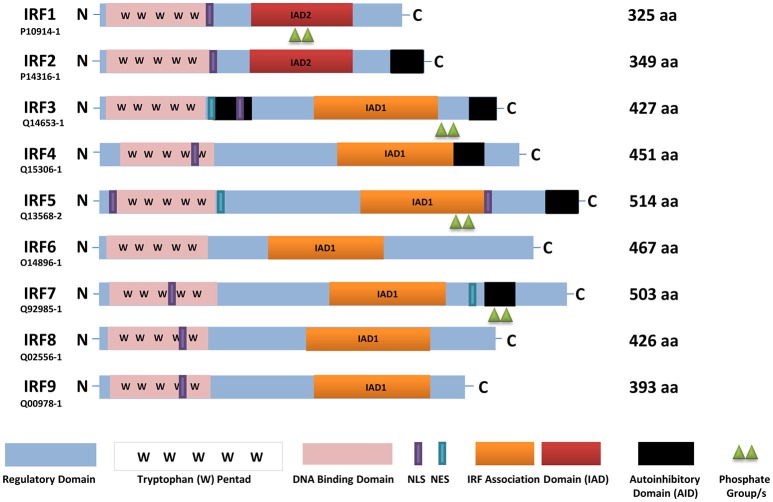
Figure 1.
A schematic representation of full-length human IRFs showing different functional domains. All IRFs harbor a DNA binding domain that contains a conserved tryptophan pentad (pink) in the N-terminus. They also contain an IRF activation domain termed either IAD1 (orange) or IAD2 (red). Other domains present are a nuclear localization signal (NLS, purple), nuclear export signal (NES, blue-green), an autoinhibitory domain (black), and a regulatory domain (blue). In this scheme, IRF activation (green triangles) is denoted as phosphorylation. The length of each IRF is indicated by the number of amino acids (aa), as found in Uniprot, with each identifier listed. IRF, interferon regulatory factor; C, carboxy terminus; N, amino terminus.