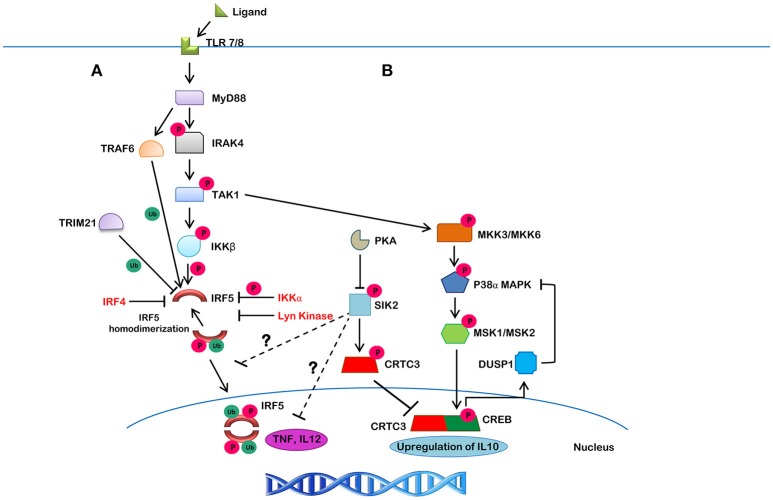
Figure 4.
The canonical IRF5 signaling pathway and its negative regulation. (A) Upon ligand binding to TLR7/8, MyD88 gets recruited in, along with IRAK1/4 and TRAF6, which leads to the autophosphorylation of IRAK4 and ubiquitination of IRF5 by TRAF6. IRAK4 then activates TAK1, which then phosphorylates IKKβ. The ubiquitinated IRF5 is then phosphorylated by IKKβ (or other kinases). This action results in homodimerization and translocation of the IRF5 homodimer to the nucleus, leading to the production of downstream cytokines. Lyn kinase, IKKα and IRF4, on the other hand, were found to negatively regulate IRF5 activity. TRIM21 is a molecule that targets IRF5 for proteasomal- or lysosomal-mediated degradation. (B) A negative feedback loop may also be involved in the suppression of IRF5-mediated inflammatory gene transcription. TAK1 initiates a series of phosphorylation events on different kinases, including MMK3/MKK6, P38α/MAPK, MSK1/MSK2, and CREB, which leads to the upregulation of IL10. SIK2, on the other hand, inhibits CRTC3 activity by phosphorylation leading to its cytosolic localization and inhibition of IL10 expression. SIK2 also inhibits inflammatory molecules, such as TNF and IL12 by unknown mechanisms that may involve inhibition of IRF5 (shown by ?).