Figure 6.
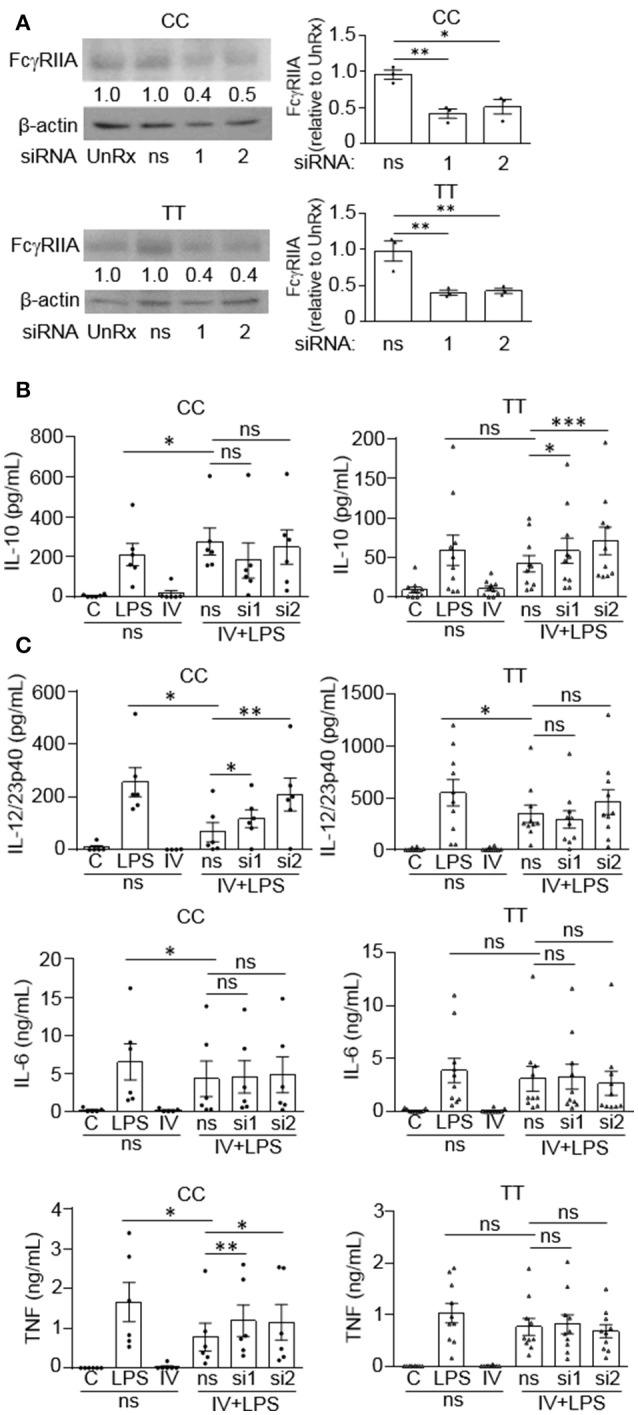
FcγRIIA prevents IVIg-induced IL-10 production in monocytes from people with the disease-associated gene variant. Monocytes from healthy control participants of the non-risk genotype (CC) and risk genotype (TT) were untreated (UnRx) or pre-treated for 48 h with a non-silencing siRNA (ns) or 2 different siRNAs to the FcγRIIA (si1 or si2). (A) Cell lysates (2.5 × 105 cells / treatment) were prepared, separated by SDS-PAGE, analyzed by western blotting with antibodies for FcγRIIA and β-actin, as a loading control. Results are representative of n = 6 experiments for the non-risk genotype (CC) and n = 10 experiments for the risk genotype (TT); Monocytes were derived from 1 participant for each independent experiment. Densitometry for FcγRIIA normalized to β-actin and relative to the control (UnRx) are averaged and shown below each band. (B,C) Monocytes pre-treated with the ns siRNA control were unstimulated [control (C)] or stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml), IVIg (5 mg/ml), or both, for 24 h, and monocytes pre-treated with FcγRIIA si1 and si2 were stimulated with IVIg (5 mg/ml) + LPS (100 ng/ml). Clarified cell supernatants were assayed for (B) IL-10, (C) IL-12/23p40, IL-6, and TNF. Data are mean ± SEM and are representative of n = 6 experiments for the non-risk genotype (CC) and n = 10 experiments for the risk genotype (TT). Monocytes were derived from 1 participant for each independent experiment and assayed in duplicate. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ns = not statistically different for the comparisons indicated. Statistical analyses were performed using a repeated measures one-way ANOVA with Dunn's multiple comparisons correction.
