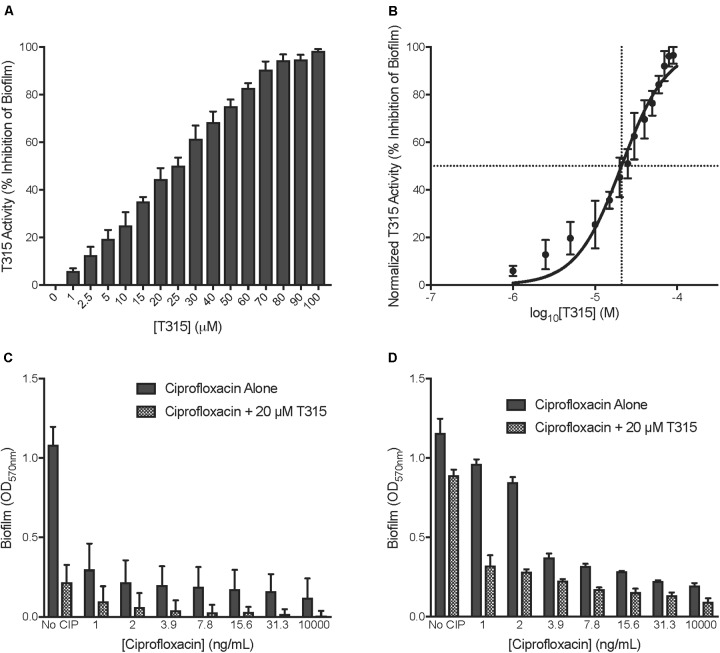
FIGURE 4.
Potential for development as anti-Typhoid carrier therapeutic. (A) Determination of EC50 of T315 against S. Typhi biofilms was achieved by exposing S. Typhi to T315 concentrations from 1 to 100 μM and examining the levels of subsequent anti-biofilm activity after 96 h. (B) The EC50 of T315 against S. Typhi biofilms is 21.0 μM (95% CI, 18.9–23.3 μM). The EC50 was calculated using GraphPad Prism 7 to plot normalized T315 activity (percent of biofilm inhibition) as a function of log10 drug concentration and fitting of the dose-response curve (log[agonist] vs. normalized response, variable slope). (C,D) Combination of 20 μM T315 and sub-MIC ciprofloxacin (various concentrations) dosing demonstrates that T315 exhibits potential to be used in conjunction with low-dose antibiotics to effectively inhibit Salmonella biofilm formation. Sub-MIC doses of ciprofloxacin were added to developing (C) S. Typhimurium and (D) S. Typhi biofilms after 6 and 24 h of biofilm growth, respectively.