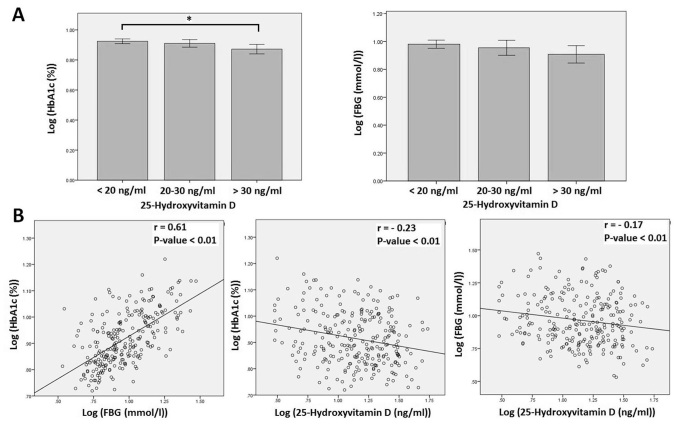
Figure 1.
Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, HbA1c and FBG levels in adults with diabetes mellitus. (A) HbA1c and FBG levels in participants according to vitamin D status. HbA1c level in participants with sufficient vitamin D (>30 ng/ml) was significantly higher than the level in participants with deficient vitamin D (<20 ng/ml). There was no significant difference in HbA1c level between participants with insufficient vitamin D (20–30 ng/ml) and participants with either sufficient or deficient vitamin D. In addition, there was no significant difference in FBG level between participants with sufficient, insufficient or deficient vitamin D. Data is expressed as mean ± standard deviation. (B) Significant correlation between HbA1c and FBG levels and significant inverse correlations between 25-hydroxyvitamin D and HbA1c and FBG levels. *P=0.02. HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; FBG, fasting blood glucose.