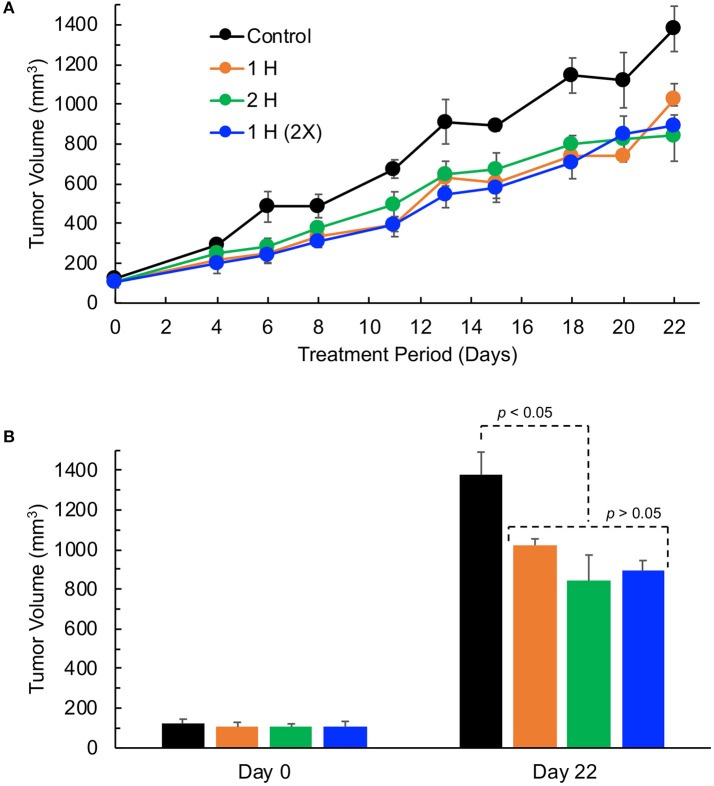
Figure 3.
TNBC xenograft tumor growth is inhibited by hyperoxygen treatment. Mice bearing TNBC xenograft tumors were exposed to varying levels of hyperoxygen by periodic administration of 100% oxygen administered via nose-cone breathing for (i) 1 h per day (1 H), (ii) 2 h per day (2 H), and (iii) 1 h twice per day (2X). Data represent tumor volume (Mean ± SEM; N = 4–5) per treatment group for the entire period (A) and on days 0 and 22 (B). All 3 modes of hyperoxygen administration show significant inhibition of tumor growth on day 22 (p-values: Control vs. 1H, 0.020; Control vs. 2H, 0.017; Control vs. 2X, 0.006); however, there are no significant differences in the tumor volumes among the treatment groups (p-values: 1H vs. 2H, 0.216; 1H vs. 2X, 0.067; 2H vs. 2X, 0.732) suggesting that 1 h per day (1 H) is as effective as the longer-duration (2 H) or multiple (2 X) treatments.