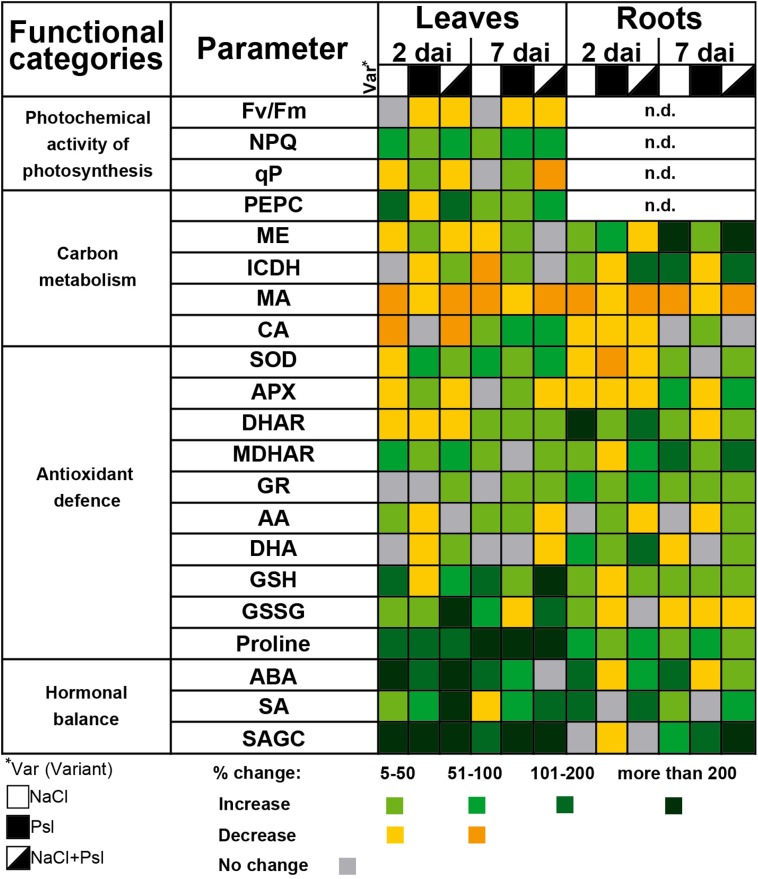
FIGURE 1.
The effect of salt stress and Pseudomonas syringae pv lachrymans (Psl) infection applied individually and in combination on photochemical activity of photosynthesis, carbon metabolism, antioxidant defense and hormonal balance in leaves and roots of cucumber plants (Chojak et al., 2012; Chojak-Koźniewska, 2017; Chojak-Koźniewska et al., 2017, 2018). Plants were pretreated for 7 days with 100 mM NaCl and then infected with Psl. Analyses were performed 2 and 7 days after inoculation (dai). Changes in contents/activities are color coded, relative to control set as 100%. Fv/Fm, maximum PSII quantum yield; NPQ, non-photochemical quenching; qP, photochemical quenching coefficient; PEPC, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase; ME, NADP-malic enzyme; ICDH, NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase; MA, malic acid; CA, citric acid; SOD, superoxide dismutase; APX, ascorbate peroxidase; DHAR, dehydroascorbate reductase; MDHAR, monodehydroascorbate reductase; GR, glutathione reductase; AA, ascorbic acid (reduced); DHA, dehydroascorbate; GSH, glutathione (reduced); GSSG, glutathione disulphide; ABA, abscisic acid; SA, free salicylic acid; SAGC, SA conjugates with glucose.