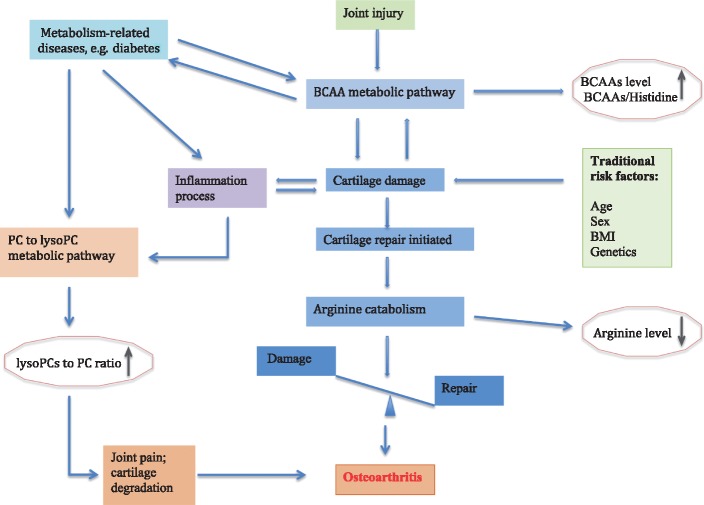
Fig. 3.
Hypothesized relationship between OA development and three promising metabolic pathways and related markers
BCAA metabolic pathway is altered because of either joint injury or articular cartilage pathology, whereas arginine catabolism is increased to activate arginine–proline pathway for cartilage repair or alternatively relatively selective utilization of arginine by other metabolic or biosynthetic process concurrent with OA process. Inflammatory factors either as an OA initiation factor or caused by OA disease process activate PC to lysoPC pathway, which mediates joint pain. Metabolism-related diseases such as diabetes alter both BCAA and PC to lysoPC metabolic pathways or mediate low-grade inflammation via lipopolysaccharide to contribute to OA, or alternatively both OA and diabetes share the same pathway. BCAA: branched chain amino acid; lysoPC: lysophosphatidylcholine; PC: phosphatidylcholine.