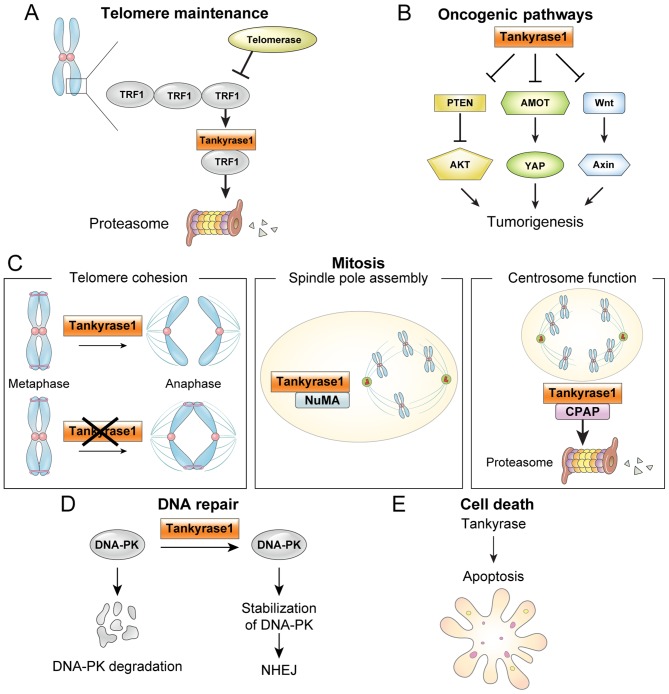
Figure 1.
Tankyrase function in cancer. (A) ADP-ribosylation of TRF1 by tankyrase 1 releases TRF1 from telomeres, and the released TRF1 is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Thus, telomere maintenance by telomerase allows continued proliferation. (B) Oncogenic pathways. Tankyrases are implicated in a number oncogenic pathways, including Wnt, YAP and AKT. (C) Mitosis. Tankyrase 1 has multiple functions in mitosis, including: i) required to resolve sister telomeres during mitosis; ii) localized to mitotic spindle poles during mitosis, where NuMA PARsylation is required for normal spindle formation and iii) regulates CPAP protein stability and function by its PARsylation. (D) DNA repair. Tankyrase 1 stabilizes the NHEJ protein DNA-PK. (E) Apoptosis. Tankyrases are involved in apoptosis, although the mechanism is unclear. TRF1, telomere repeat binding factor 1; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; YAP, yes-associated protein; AMOT, angiomotins; NuMA, nuclear mitotic apparatus; CPAP, centrosomal P4.1-associated protein; DNA-PK, DNA-dependent protein kinase; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining.