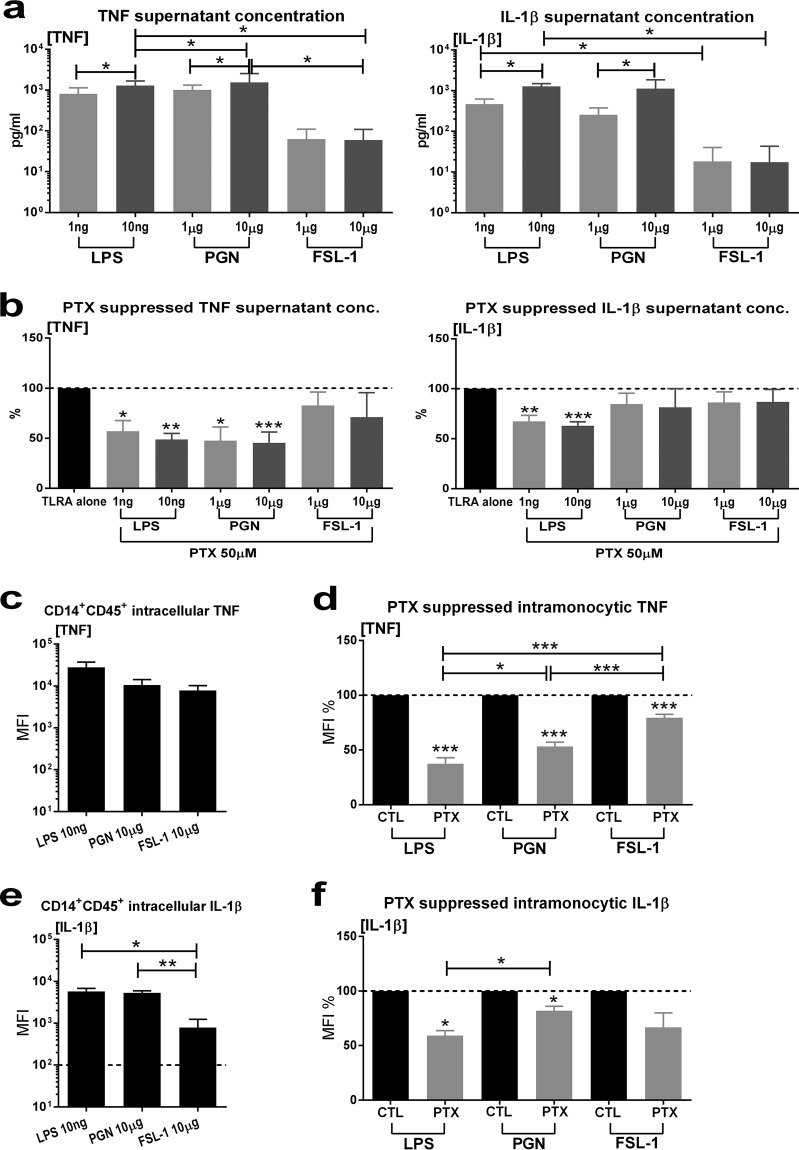
FIG 7.
PTX inhibited TLR2- and TLR4-mediated proinflammatory cytokine production in newborn cord blood and cord blood monocytes. Cord blood (n = 5) was stimulated with purified TLR2 (PGN and FSL-1) or TLR4 (LPS) agonists and simultaneously treated with PTX or vehicle control. (a) TLR2 and TLR4 agonist-induced proinflammatory cytokines in cord blood culture supernatants. (b) Effect of PTX on TLR2 and TLR4 agonist-induced TNF and IL-1β in cord blood culture supernatants. (c) TLR2 and TLR4 agonist-induced intracellular TNF in cord blood monocytes. (d) Inhibition of TLR2- and TLR4-mediated intramonocytic TNF by PTX. (e) TLR2 and TLR4 agonist-induced intracellular IL-1β in cord blood monocytes. (f) Inhibition of TLR2 and TLR4 agonist-induced intramonocytic IL-1β by PTX. Cytokine concentrations and MFI values of treated samples are expressed as percentages compared to untreated samples stimulated with TLR agonists alone, which were defined as 100%. Significant differences between treated versus untreated samples and between samples stimulated with TLR2 versus TLR4 agonists are indicated (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).