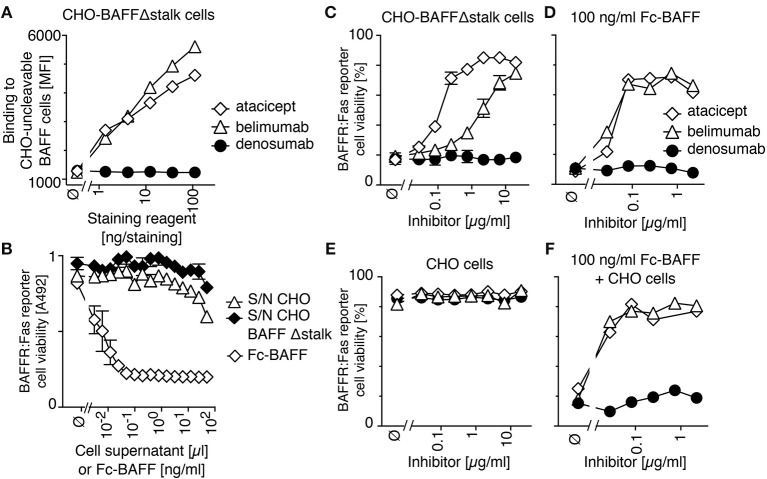
Figure 2.
Belimumab binds and partially inhibits membrane-bound BAFF lacking the stalk region expressed in CHO cells. (A) CHO cells stably expressing uncleavable BAFF Δstalk were stained with the indicated amounts of atacicept, belimumab or denosumab. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of staining was monitored. Single measures were performed. Experiment performed 3 times. (B) BAFFR:Fas reporter cells were exposed to titrated amounts of conditioned supernatants of CHO cells with or without expression of uncleavable BAFF Δstalk, or to recombinant soluble BAFF (Fc-BAFF) added as a positive control. After overnight incubation, cell viability was monitored with the PMS/MTS test. Mean ± SEM of triplicates. Experiment performed twice. (C) CFSE-labeled BAFFR:Fas reporter cells were co-cultured with CHO cells expressing uncleavable BAFF in the presence of increasing concentrations of atacicept, belimumab or denosumab. Cell viability after overnight incubation was measured by flow cytometry. Measures are duplicates (mean ± SEM). Experiment performed twice. (D) Same as panel C, except that uncleavable BAFF Δstalk cells were replaced by a lethal dose of Fc-BAFF (100 ng/ml). Single measures were performed. Experiment performed twice. (E) Same as panel C, except that uncleavable BAFF Δstalk cells were replaced by control CHO cells. Single measures were performed. Experiment performed twice. (F) CFSE-labeled BAFFR:Fas reporter cells were co-cultured overnight with CHO cells and 100 ng/ml of Fc-BAFF, in the presence of inhibitors at the indicated concentrations. Single measures were performed. Experiment performed twice.