Figure 6.
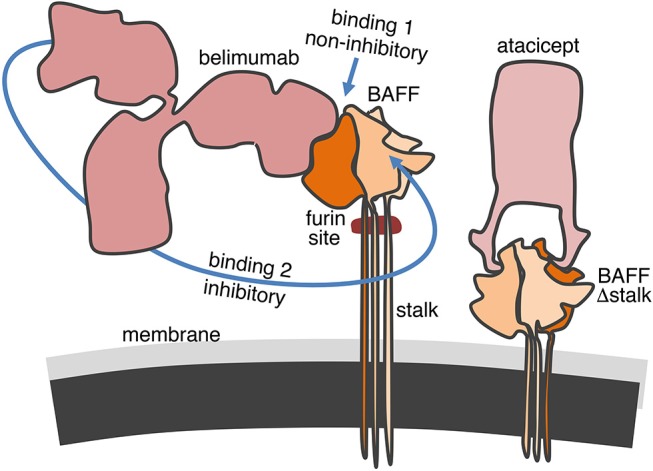
Hypothetical model for the binding of belimumab and atacicept to membrane-bound BAFF. The 66 amino acids-long stalk of BAFF contains the furin cleavage site and, if linear and extended, could have three times the height of the globular TNF homology domain. In contrast, the engineered stalk-less BAFF is much closer to the membrane. Atacicept binds BAFF from the side opposite to the membrane and has free access regardless of the length of the stalk. Belimumab is not only bulkier but also binds more on the side of BAFF along the entire height of the TNF homology domain. The first binding of belimumab to membrane-bound BAFF is probably always easy, but insufficient to inhibit the biological activity of BAFF. Inhibition only takes place upon binding of the second arm of the antibody to membrane-bound BAFF. Movements of the antibody to reach its second binding site might be compromised for steric hindrance reasons if BAFF is located too close to the cell membrane in BAFF Δstalk.
