Figure 3.
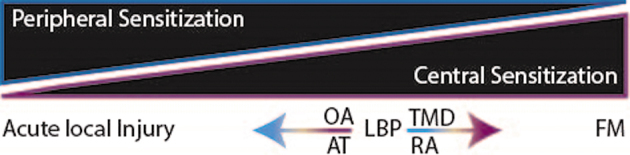
In pain conditions, peripheral sensitization and central sensitization vary across a continuum. Sensitization of the peripheral nervous system contributes to a large proportion of pain with an acute localized injury, whereas sensitization of the central nervous system contributes to a large proportion of pain with chronic widespread pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia (FM). For other diagnoses, depicted in the midrange as low back pain (LBP), osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Achilles tendinopathy (AT), and temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD), people can have high levels of peripheral sensitization, high levels of central sensitization, or both.
