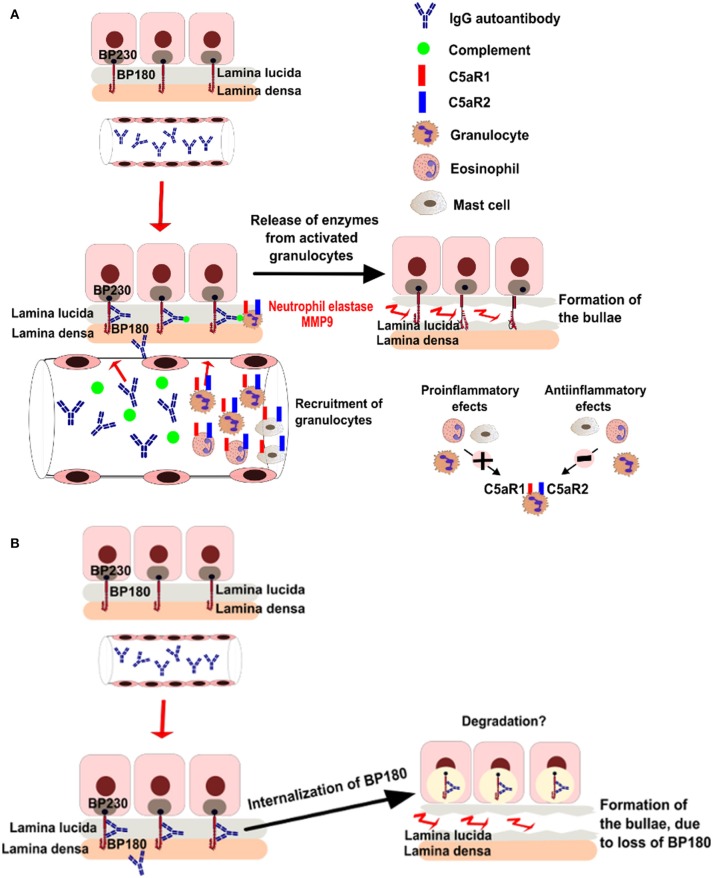
Figure 1.
Putative pathogenic mechanisms of blistering in bullous pemphigoid. (A) Complement dependent pathways of bullae formation. Binding of IgG autoantibodies at the dermal epidermal junction leads to complement activation and recruitment of neutrophils. Activated neutrophils release proteolytic enzymes, inducing dermal-epidermal separation. (B) Complement-independent pathways of bullae formation. Binding of IgG autoantibodies to BP180 leads to depletion of the protein by internalization.