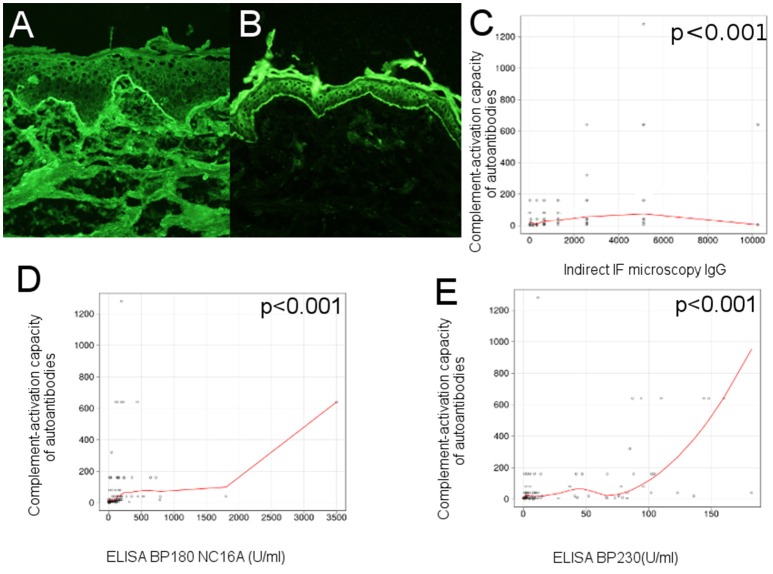
Figure 2.
Complement-activation potential of circulating IgG anti-basement membrane zone autoantibodies correlates with their levels in bullous pemphigoid patients. (A) Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy on normal human foreskin shows binding of IgG autoantibodies from the serum of a BP patient at the dermal-epidermal junction. (B) Complement-binding test shows linear C3 deposits along the basement membrane of normal human foreskin, when using serum from a BP patient, demonstrating activation of complement by IgG autoantibodies. Relation of ex vivo complement-activating capacity of autoantibodies and (C), titers of circulating IgG anti-basement membrane zone autoantibodies, measured by indirect IF microscopy; (D), titers of circulating IgG anti-BP180 NC16A, measured by ELISA; (E), titers of circulating IgG anti-BP230, measured by ELISA (n = 90). The red line represents the locally weighted scatterplot smoothing line.